Global Marine Ecosystem Pressure Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
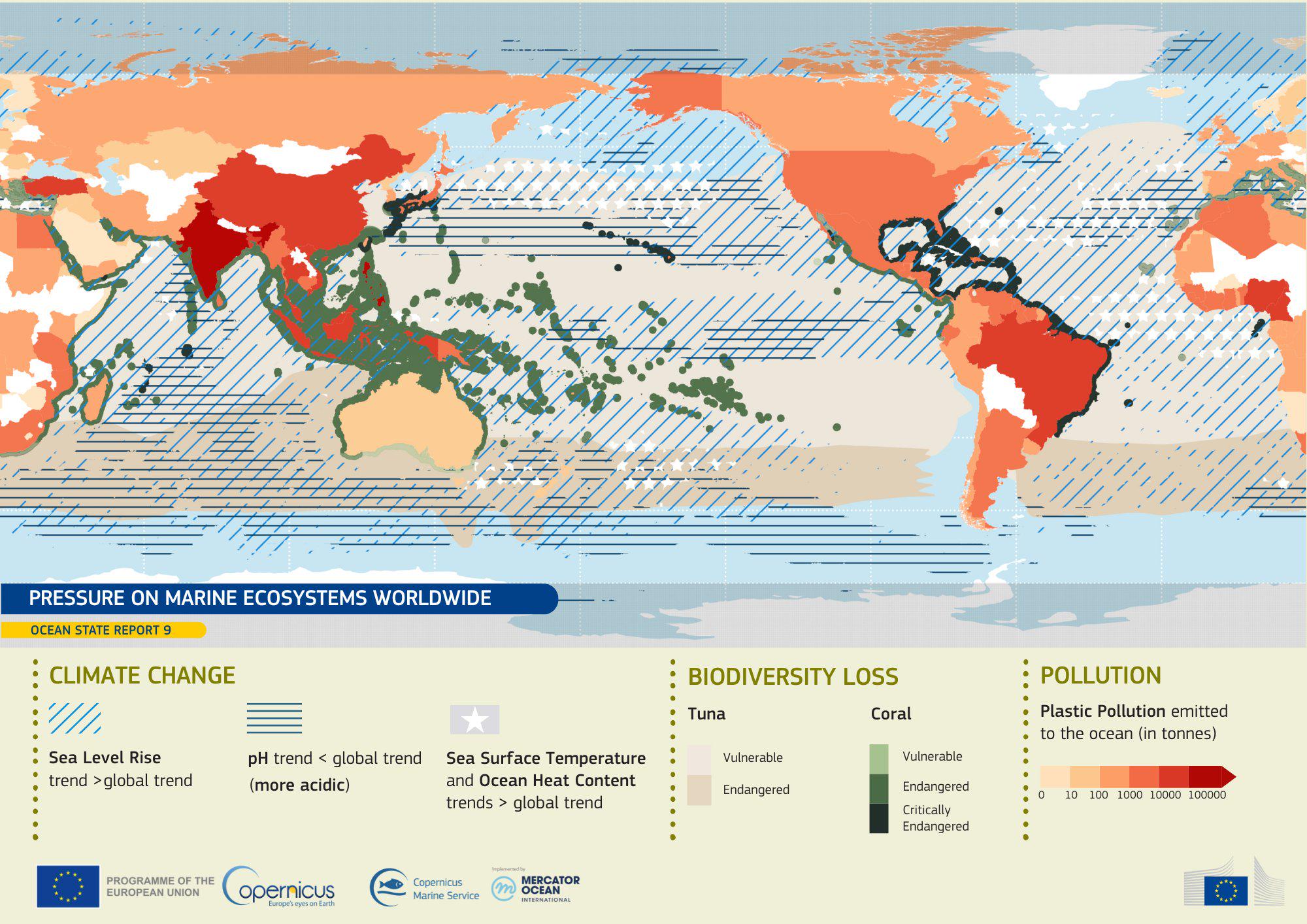
The "Pressure on Marine Ecosystem Worldwide" map provides a comprehensive visualization of the diverse threats facing marine environments across the globe. It highlights areas where human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change pose significant risks to marine biodiversity. The map employs color gradients to indicate the severity of pressure in various regions, allowing viewers to quickly identify hotspots of ecological concern. With oceans covering more than 70% of our planet's surface, understanding these pressures is crucial for maintaining the health of our marine ecosystems.
Deep Dive into Marine Ecosystems
Marine ecosystems are among the most complex and vital systems on Earth, supporting a staggering array of life forms, from the tiniest plankton to the largest whales. They play a crucial role in regulating the global climate, producing oxygen, and providing food and livelihoods for millions of people. However, these ecosystems are under intense pressure from various anthropogenic factors.
Overfishing is one of the most significant threats. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately 34% of global fish stocks are overexploited, depleted, or recovering from depletion. This unsustainable practice not only affects fish populations but also disrupts the entire food web, leading to declines in species that rely on these fish for survival. Have you ever wondered why certain fish are becoming harder to find? The answer often lies in our fishing practices.
Pollution, particularly plastic waste, is another pressing issue. An estimated 8 million tons of plastic enter the oceans each year, adversely affecting marine life. Sea turtles, for example, often mistake plastic bags for jellyfish, leading to fatal consequences. What’s fascinating is that microplastics, tiny plastic particles that result from the breakdown of larger plastics, are now found in the most remote marine environments, highlighting the pervasive nature of this issue.
Climate change is perhaps the most daunting challenge facing marine ecosystems. Rising sea temperatures lead to coral bleaching, affecting the vibrant coral reefs that serve as biodiversity hotspots. Additionally, ocean acidification, a direct result of increased carbon dioxide absorption by seawater, is weakening the shells of marine organisms like mollusks and disrupting marine food chains.
Given these pressures, the importance of marine conservation efforts cannot be overstated. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are a critical tool in mitigating these threats, helping to preserve biodiversity and restore fish populations. Interestingly, studies have shown that well-managed MPAs can lead to increased fish stocks and improved resilience against climate change.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see that pressure on marine ecosystems varies significantly by region. For example, the Caribbean Sea is marked by intense pressure due to a combination of overfishing and pollution from tourism and coastal development. Coral reefs in this region are facing unprecedented challenges, with bleaching events becoming more frequent. Conversely, the North Atlantic Ocean shows signs of recovery in certain areas due to successful fishing regulations and protective measures.
In contrast, the Pacific Ocean presents a mixed picture. While areas like the Great Barrier Reef in Australia face severe threats from climate change and pollution, other regions are benefiting from robust conservation efforts and community engagement. The map also indicates that regions with high levels of industrial activity, such as parts of Southeast Asia, experience heightened pollution levels, which further exacerbates the impact on marine biodiversity.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the pressures on marine ecosystems is essential for several reasons. Firstly, these ecosystems are crucial for food security, especially for coastal communities that rely on fishing for their livelihoods. Moreover, healthy oceans contribute to global carbon regulation, helping mitigate climate change impacts.
As we reflect on the future, it is vital to recognize that trends indicate increasing human activity in marine environments. With the global population expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the demand for marine resources will only intensify. Therefore, proactive measures, such as implementing sustainable fishing practices and expanding MPAs, will be essential in safeguarding these critical ecosystems.
In conclusion, the "Pressure on Marine Ecosystem Worldwide" map serves as a vital reminder of the challenges our oceans face. By understanding these pressures, we can better advocate for policies and practices that protect marine life and ensure the sustainability of our oceans for future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 12, 2025
- Views
- 30
Comments
Loading comments...