Female Genital Mutilation Prevalence Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
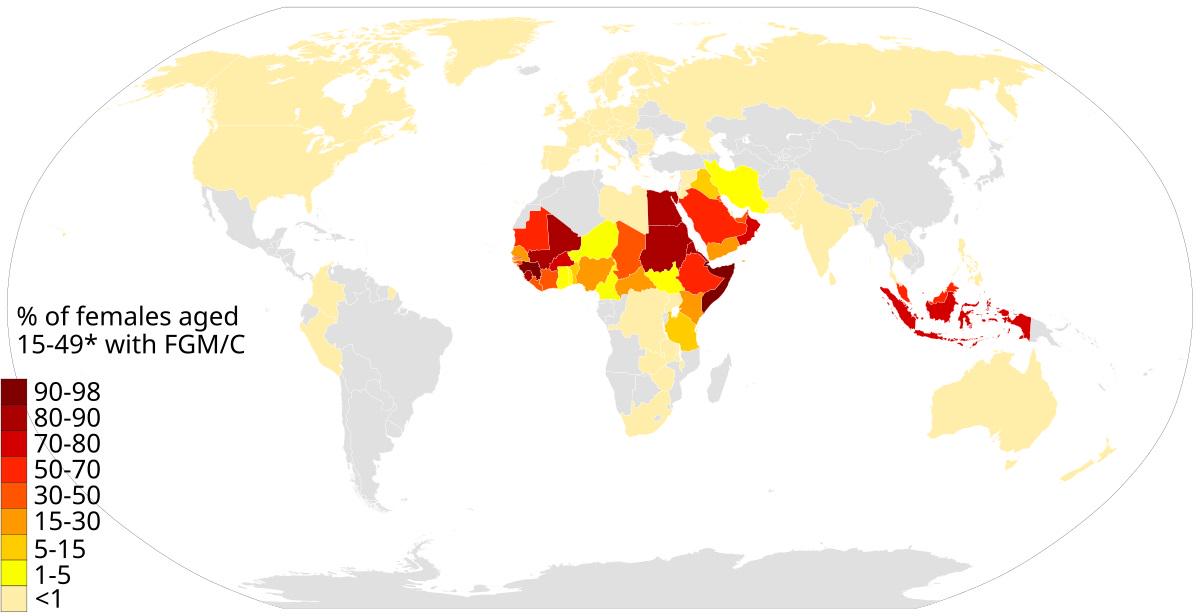
What This Map Shows
The "Prevalence of Female Genital Mutilation Worldwide" map provides a stark visualization of the regions where this deeply rooted cultural practice occurs. It highlights the varying percentages of women and girls affected by female genital mutilation (FGM) across different countries and regions. The map is an essential tool for understanding the magnitude of this issue, which affects millions of women and girls globally.
Deep Dive into Female Genital Mutilation
Female genital mutilation refers to the partial or total removal of the external female genitalia or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons. This practice, often justified by cultural, religious, or social norms, is prevalent mainly in parts of Africa, the Middle East, and some Asian countries. What’s fascinating is that FGM is not just a health issue; it encompasses human rights, gender equality, and social justice.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 200 million women and girls alive today have undergone FGM in 30 countries where the practice is most common. The prevalence rates can vary significantly. For example, in Somalia, nearly 98% of women have been subjected to this practice, while in countries like Egypt and Sudan, the rates, although still high, are slightly lower, hovering around 87% and 87% respectively. On the other hand, some countries like Nigeria show a wide range of prevalence across different regions, indicating that cultural acceptance of FGM can differ even within the same nation.
Interestingly, despite the deep-rooted cultural significance of FGM, there is a growing movement against it. Activism and education initiatives have led to a decrease in prevalence rates in some areas. For instance, in many urban centers, there is a notable decline in the practice due to increasing awareness and advocacy for women's rights. However, resistance remains strong in rural areas where traditional beliefs are deeply entrenched.
Health complications arising from FGM are severe and can include chronic pain, infections, complications during childbirth, and even death. The psychological impact is equally damaging, often leading to long-term trauma. These health risks emphasize the urgent need for global awareness and intervention strategies.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map by regions, the differences in prevalence rates are striking. In Africa, the highest concentrations of FGM are found in the northeastern and western parts. Countries like Somalia, Djibouti, and Mali report rates above 90%. In contrast, countries like Kenya and Tanzania are witnessing a decline in rates due to concerted efforts by governments and NGOs to educate communities about the risks associated with FGM.
In the Middle East, particularly in countries like Egypt and Sudan, FGM remains prevalent, but there are ongoing discussions about its legality and necessity. Egypt has seen some legislative changes, although enforcement remains inconsistent. In contrast, in the Middle East, particularly in Yemen and Iraq, the practice is less common, suggesting cultural variations even among Muslim-majority countries.
Interestingly, the prevalence of FGM is not limited to developing countries. In some Western countries, immigrant communities from regions where FGM is practiced may continue the tradition, raising complex legal and ethical challenges in terms of cultural preservation versus human rights.
Significance and Impact
Addressing the issue of FGM is critical not only for the health and rights of women and girls but also for broader social development. FGM is recognized as a violation of human rights and an impediment to achieving gender equality. The map serves as a reminder of the work that still needs to be done to eradicate this practice.
Current trends indicate a gradual decline in the prevalence of FGM due to increased awareness, education, and the empowerment of women and girls in affected regions. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has hindered progress, as many health and education services were disrupted, potentially leading to a rise in cases.
Looking to the future, it's essential to continue advocacy and education efforts. The map is not just a representation of data; it’s a call to action for governments, NGOs, and communities worldwide to work collectively towards ending FGM and protecting the rights of women and girls everywhere. Have you noticed how maps can often highlight issues that are otherwise overlooked? This is a perfect example of how geography can play a crucial role in social change.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 8, 2025
- Views
- 42
Comments
Loading comments...