Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
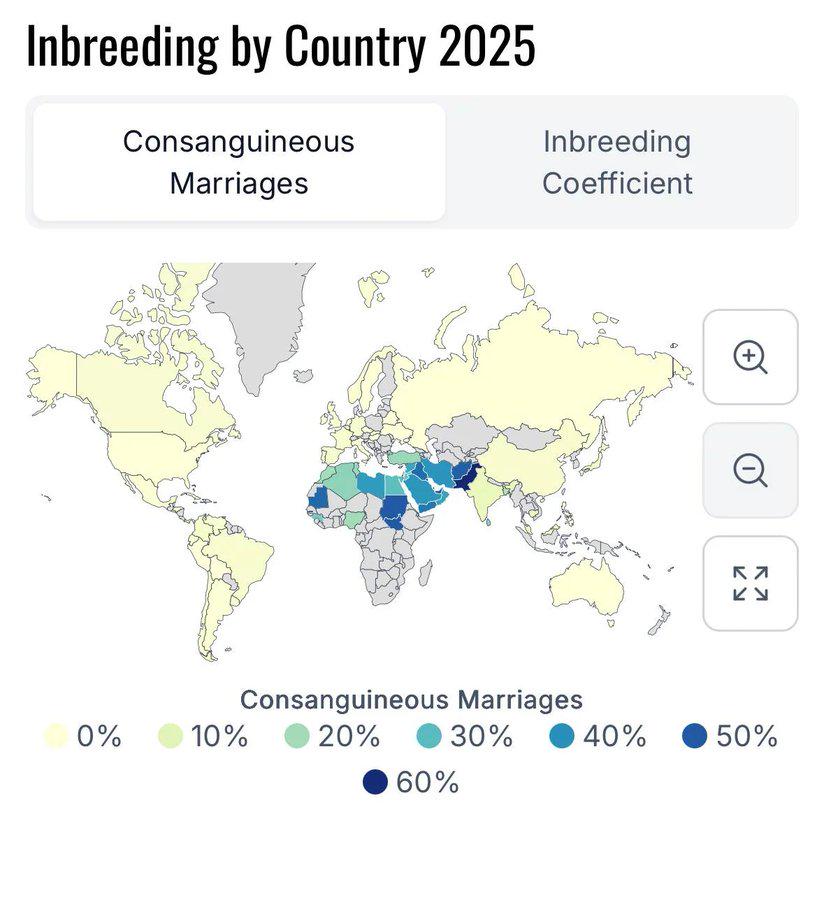
What This Map Shows
The "Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map" provides a visual representation of the rates of inbreeding across different countries, highlighting the genetic implications of consanguinity in various populations. It uses an array of colors and intensity to indicate the prevalence of inbreeding, allowing viewers to quickly grasp how different nations compare. This topic is not merely a statistical curiosity; it has profound implications for genetic diversity, public health, and cultural practices around the world.
Deep Dive into Inbreeding and Its Implications
Inbreeding refers to the mating of individuals who are closely related genetically. This practice can lead to a higher likelihood of offspring inheriting harmful genetic traits, which can manifest in various health issues, reduced fertility, and increased susceptibility to diseases. The biological principle behind this is relatively straightforward: mating between close relatives increases the chances of offspring receiving two copies of deleterious alleles, which can lead to genetic disorders.
Interestingly, in some cultures, inbreeding is a social norm for reasons ranging from preserving family wealth to maintaining cultural identity. For example, certain communities may practice cousin marriages, which can perpetuate specific genetic traits—both positive and negative—within the population. However, the consequences of inbreeding are not uniform; they vary significantly across different regions and cultures.
Globally, the prevalence of inbreeding tends to be higher in isolated communities where there are fewer options for partners. For instance, some areas in the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia report higher rates of consanguinity, often exceeding 20% in certain populations. According to studies, the genetic effects of inbreeding can lead to increased rates of congenital disabilities and hereditary diseases in these communities. In contrast, more diverse nations, particularly those with significant immigration and urban migration, typically exhibit lower rates of inbreeding.
Additionally, inbreeding coefficients, a numerical measure of the likelihood that two alleles inherited by an offspring are identical by descent, can offer insight into the genetic health of populations. A higher inbreeding coefficient often correlates with reduced genetic diversity, which can be detrimental in the face of environmental changes or disease outbreaks.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can observe significant regional variations in inbreeding rates. For instance, North Africa stands out with some of the highest concentrations of inbreeding, particularly in countries like Egypt and Libya. In these nations, social customs and historical practices have contributed to elevated rates of cousin marriages.
In contrast, Northern Europe, characterized by higher levels of social mobility and increased genetic mixing due to migration, shows much lower inbreeding rates. Countries like Sweden and Norway report inbreeding coefficients that are remarkably lower than their Southern counterparts. Interestingly, this aligns with public health initiatives and educational campaigns that promote genetic awareness and the health risks associated with inbreeding.
In sub-Saharan Africa, the picture is more complex. While certain communities exhibit high rates of inbreeding due to cultural practices, others are more diverse due to population movements and intermarriage among different ethnic groups. For instance, in regions with high levels of urbanization, such as parts of Nigeria, inbreeding rates may decline as individuals seek partners outside their immediate familial or ethnic circles.
Significance and Impact
Understanding inbreeding and its implications is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, from a public health perspective, it can inform policies aimed at reducing the prevalence of genetic disorders in populations with high rates of consanguinity. This knowledge can also guide healthcare providers in offering better genetic counseling to families at risk.
Moreover, as globalization continues to influence migration patterns, the dynamics of inbreeding may shift. Countries that currently exhibit high inbreeding rates may see changes as individuals increasingly marry outside their communities. This could enhance genetic diversity, which is vital for the resilience of populations against diseases and environmental changes.
In conclusion, the "Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map" serves as an essential tool for understanding the genetic landscape of our world. By engaging with this topic, we can appreciate the complex interplay between culture, genetics, and health, paving the way for more informed discussions and policies in the future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 8, 2025
- Views
- 42
Comments
Loading comments...