Main Sources of Electricity Around the World Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
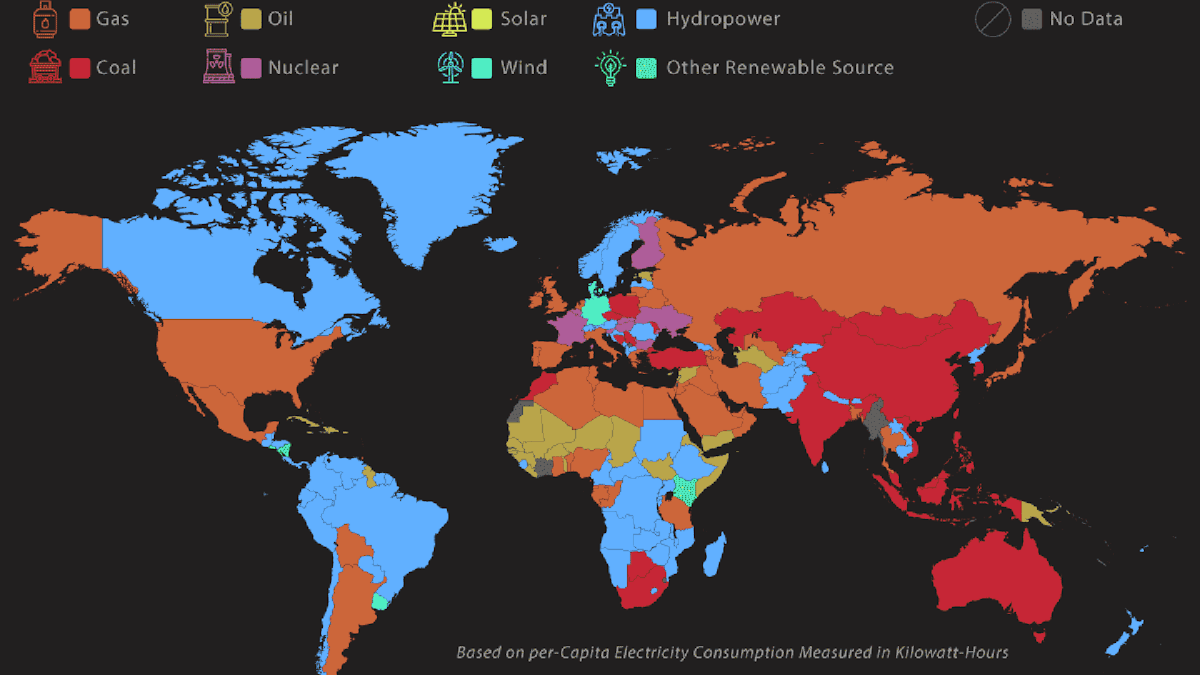
What This Map Shows
The "Main Sources of Electricity Around the World" map provides a comprehensive overview of how different countries generate their electricity. By visually representing the primary energy sources—such as fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewable energy—it highlights the energy landscape across various nations. This visualization offers insight into the global shift towards renewable energy, the continued reliance on fossil fuels, and the unique energy strategies adopted by individual countries. Understanding these patterns is essential for grasping the broader implications of energy production on climate change, economic stability, and technological advancements.
Deep Dive into Electricity Sources
Electricity generation is a critical aspect of modern civilization, powering homes, industries, and infrastructure. The sources of electricity can be broadly categorized into three main types: fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable resources. Fossil fuels, which include coal, oil, and natural gas, have historically dominated the global energy scene. For instance, countries like the United States, China, and India still rely heavily on coal and natural gas for their electricity needs, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Interestingly, while fossil fuels are still prevalent, there is a noticeable shift towards more sustainable sources. Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy, are gaining traction worldwide. For example, countries like Denmark and Germany are leading the way in wind energy production, while China is a frontrunner in solar power installations. In fact, as of 2023, China accounts for over 30% of global solar energy capacity, which illustrates a significant commitment to renewable sources.
Nuclear energy, another key player in the electricity generation arena, also plays a vital role in reducing carbon footprints. Nations like France and Japan utilize nuclear power extensively, providing a substantial portion of their electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, public perception and safety concerns, particularly in the wake of disasters like Fukushima, continue to shape the debate around nuclear energy's future.
As we delve deeper into the statistics, it is fascinating to note that renewable energy sources have experienced exponential growth over the past decade. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global renewable electricity generation has doubled between 2010 and 2020, and projections indicate that this trend will continue as technology advances and investment increases. This shift is not merely environmental; it also represents a shift in economic paradigms, where jobs in renewable sectors are rapidly increasing, often outpacing those in fossil fuel industries.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, we can observe distinct patterns in electricity generation across different regions. For instance, North America still relies heavily on fossil fuels, with natural gas being a dominant source in the U.S. and Canada. However, states like California are leading the charge in renewable energy, with ambitious goals to achieve 100% clean energy by 2045.
In contrast, Europe is making significant strides towards sustainability, with countries like Norway and Sweden generating most of their electricity from hydro and wind power. The European Union has set ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions, promoting a transition from coal to renewables that is already evident in countries like Germany, which has cut coal use significantly.
Asia presents a mixed bag. While countries like India are ramping up renewable energy efforts, they still depend heavily on coal for electricity generation. On the other hand, Japan, following its post-Fukushima policy shift, is cautiously reintroducing nuclear energy while expanding renewable capacities.
Interestingly, Africa is witnessing a unique scenario. Many countries are rich in renewable resources, yet they struggle with electricity access. Nations like Kenya are leading the way in geothermal energy, while solar power is becoming increasingly popular in off-grid communities. The map highlights these contrasts, showcasing both the potential and challenges faced by regions across the globe.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the main sources of electricity around the world is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, the choice of energy source directly impacts a country's carbon footprint and its role in combating climate change. With climate change becoming an increasingly urgent global issue, transitioning to renewable energy is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, energy security is a paramount concern for many nations. Countries that rely heavily on imported fossil fuels may face vulnerabilities due to geopolitical tensions or price fluctuations. In contrast, those investing in local renewable resources can enhance their energy independence and create jobs in emerging sectors.
Looking ahead, the global energy landscape is poised for transformation. As technology advances and public awareness of climate issues grows, we can expect a continued transition towards renewables. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that renewable energy could provide up to 80% of the world's electricity by 2050, a shift that could redefine economies and societies.
In summary, this map not only illustrates where electricity comes from but also serves as a reminder of the urgent need to rethink our energy practices. By understanding these sources, we can better navigate the complexities of energy production and its repercussions on our planet and future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 2, 2025
- Views
- 40
Comments
Loading comments...