Map of Hair Colours in Human Populations

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
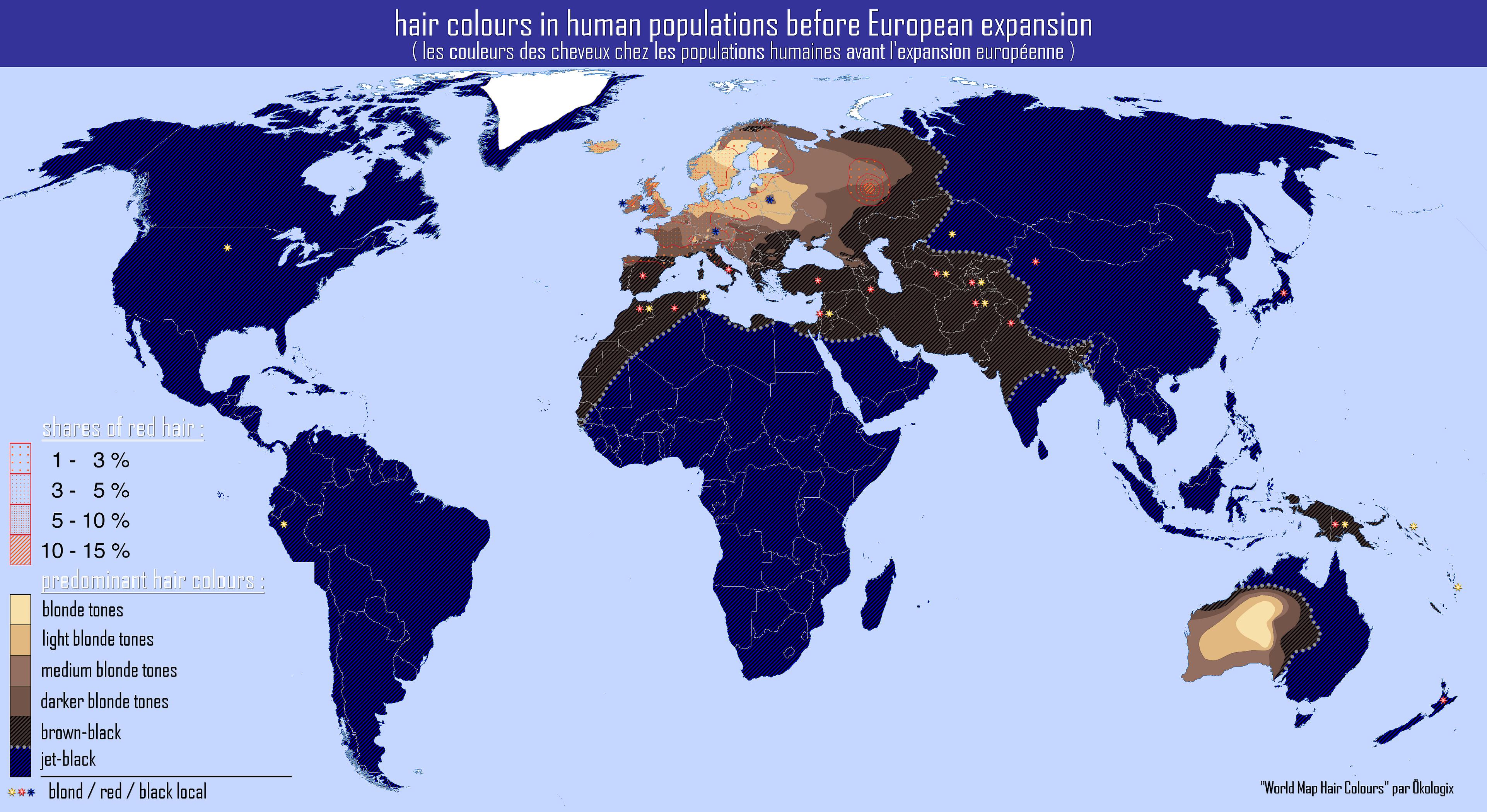
What This Map Shows
This map provides a visual representation of the distribution of various hair colors among human populations prior to European expansion. It highlights the prevalence of different shades—ranging from black and brown to blonde and red—across regions, allowing us to explore the genetic diversity and adaptations of early human societies. By examining this map, we can see not only where these hair colors were common but also infer historical migration patterns and the influence of environmental factors on human genetics.
Deep Dive into Hair Colour Diversity
Hair color in humans is a fascinating subject that reflects a complex interplay of genetics, environment, and evolution. The primary colors we see today—black, brown, blonde, and red—are the result of varying levels of melanin produced in the hair follicles. Melanin is a pigment that not only affects hair color but also skin tone and eye color. Interestingly, the distribution of these hair colors can tell us much about human adaptation to different environments.
Black hair is the most common globally, particularly in populations originating from Africa, Asia, and parts of the Americas. This prevalence is largely due to the high levels of eumelanin, which provides greater UV protection. In contrast, lighter hair colors such as blonde and red are more prevalent in northern European populations, where lower sunlight levels may have led to evolutionary adaptations favoring lighter pigmentation. This phenomenon is known as the 'Vitamin D hypothesis,' suggesting that lighter skin and, consequently, lighter hair could have been advantageous for the synthesis of Vitamin D in regions with less sunlight.
The genetic basis for hair color is influenced by multiple genes, with the most notable being the MC1R gene, which is linked to red hair and fair skin. Variations in this gene can lead to the unique phenotypic expressions we observe today. Interestingly, red hair, which is relatively rare globally, has its highest frequencies in the Celtic regions of Ireland and Scotland.
Furthermore, the map shows that variations in hair color are not merely random. They are shaped by geographical and cultural factors. For instance, in regions where there was significant intermingling of populations—like in the Mediterranean basin—mixed hair colors can be observed, reflecting a blend of genetic traits.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map regionally, we can observe distinct patterns. In Africa, the predominance of black hair is evident, showcasing the genetic diversity within the continent. Interestingly, in regions with significant historical trade routes, such as North Africa and the Middle East, we might find a blend of hair colors due to the mingling of different ethnic groups.
In Europe, the contrast between northern and southern populations stands out. Northern Europeans typically display lighter hair colors, while southern populations, particularly in Mediterranean countries, are more likely to have darker hair. This divergence can be attributed to both historical migrations and climatic adaptations.
Moving to Asia, the map reveals a predominance of black and dark brown hair, with notable exceptions in specific populations like the Mongolians, who may show lighter shades due to genetic drift and adaptation to their unique environments. In contrast, the indigenous populations of the Americas exhibit a range of hair colors, primarily black and brown, influenced by their ancestors' migrations from Asia across the Bering Land Bridge.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of hair colors in human populations before European expansion is significant for several reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on human genetic diversity and how adaptation to different environments shapes our physical characteristics. This knowledge is crucial in fields like anthropology, genetics, and even medicine, as it helps us understand the evolutionary pressures that have influenced human populations.
Moreover, this topic has implications in today's world. As globalization continues, we see a blending of traits and features across populations, leading to new variations in hair color and other physical characteristics. This raises questions about identity and cultural heritage, as people navigate their connections to ancestral traits amidst a rapidly changing world.
As we look to the future, it's essential to consider how ongoing genetic studies and advancements in technology will continue to unveil the mysteries of human diversity. Have you ever wondered how our understanding of hair colors might evolve with new genetic discoveries? The past is a key to understanding our present and future, and maps like these serve as vital tools in that exploration.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 1, 2025
- Views
- 34
Comments
Loading comments...