China's Ideological Spectrum by City Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
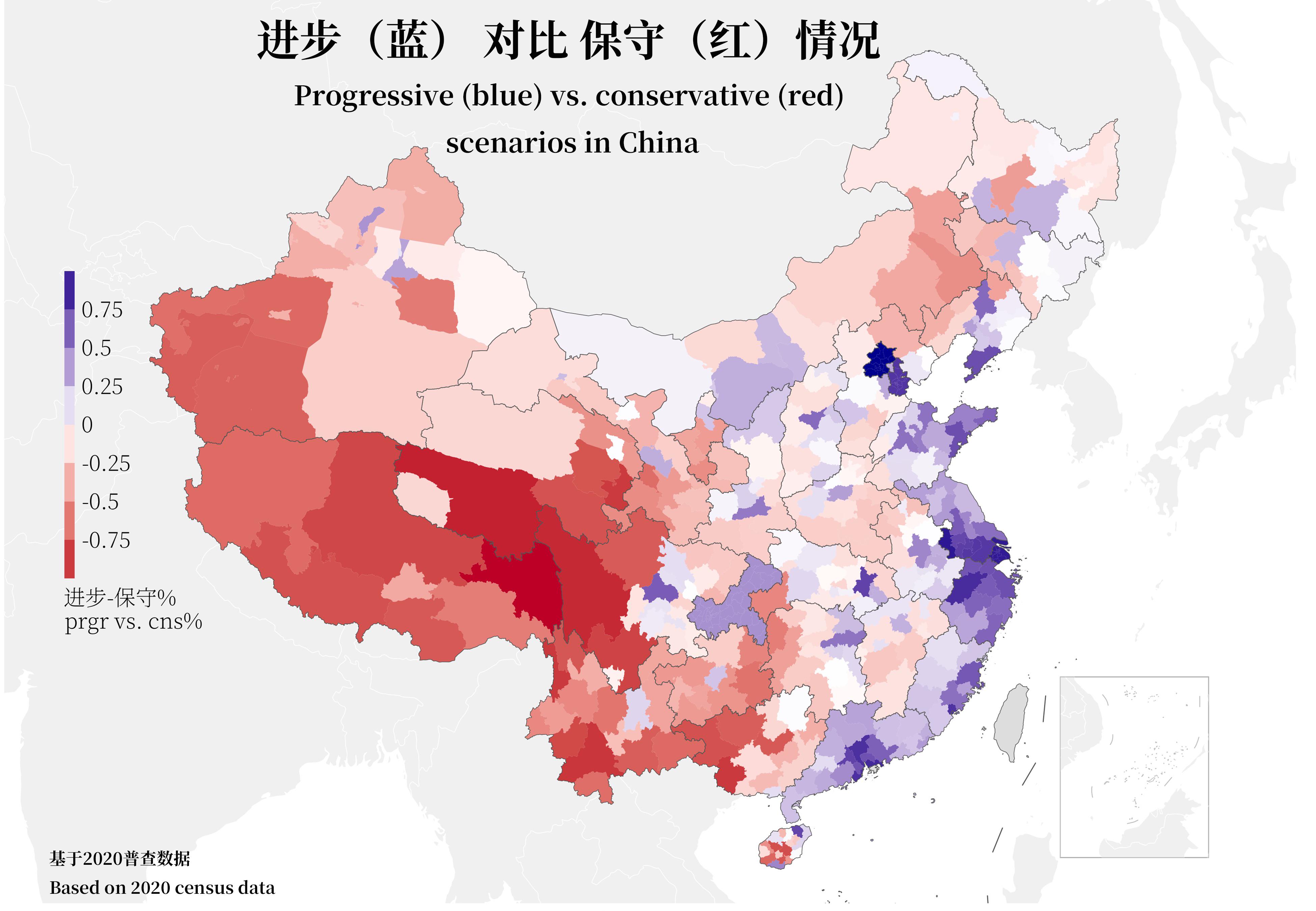
What This Map Shows
This visualization presents a detailed overview of China's ideological spectrum, breaking it down by city based on data from the 2020 census. It highlights the varying political and ideological leanings across different urban centers, providing insight into the diverse beliefs and values held by residents in these areas. As we delve into the ideological landscape of China, we can gain a deeper understanding of how geography influences political perspectives and societal norms.
Deep Dive into China's Ideological Landscape
China's ideological spectrum is far from monolithic. It encompasses a wide range of beliefs influenced by historical, cultural, and social factors. At the core, China's political ideology is heavily shaped by the Communist Party's principles, but local variations emerge due to regional identities, economic conditions, and educational backgrounds.
Interestingly, urban areas often exhibit a more progressive attitude compared to rural regions. For instance, cities like Beijing and Shanghai, known for their cosmopolitan environments and higher education levels, tend to lean towards more liberal ideologies. According to the 2020 census data, these cities show a significant percentage of residents identifying with progressive social policies and reform-oriented ideas.
Conversely, second-tier cities and rural regions may reflect more conservative or traditional ideologies. This is often due to a combination of factors such as lower educational attainment, economic reliance on agrarian lifestyles, and stronger adherence to traditional values. For example, cities in the interior provinces like Henan or Anhui frequently report a higher inclination toward conservative ideologies, emphasizing family values and local customs.
Moreover, the impact of globalization and technology cannot be overlooked. Urban centers are hubs of information and cultural exchange, which fosters a more open-minded populace. This exposure often leads residents to adopt international perspectives on issues such as human rights, environmentalism, and economic reforms. Additionally, the rise of social media platforms has allowed for greater discourse and the dissemination of diverse ideological viewpoints, which can further challenge traditional norms.
Data from the census indicates that younger generations, particularly in urban areas, are more likely to advocate for progressive causes, including gender equality and LGBTQ+ rights. This generational shift is critical, as it hints at a potential transformation of China's ideological landscape in the coming decades.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the ideological spectrum by region reveals intriguing contrasts. In the southern provinces, such as Guangdong and Fujian, the influence of economic modernization has fostered a more liberal outlook. Cities like Shenzhen, often dubbed China's Silicon Valley, exhibit a high concentration of progressive thought, fueled by a young, tech-savvy population.
In contrast, the northwestern regions, including Xinjiang and Gansu, tend to showcase more conservative views. The cultural and ethnic diversity in these areas contributes to a blend of traditional beliefs and resistance to rapid change, reflecting a slower adaptation to the more liberal ideologies found in coastal cities.
Furthermore, major cities like Chengdu and Wuhan, while geographically central, display a mixed ideological spectrum. Chengdu, known for its relaxed lifestyle and vibrant culture, leans towards progressivism, whereas Wuhan, with its historical significance as an industrial hub, shows a more conservative bent influenced by its working-class roots.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ideological spectrum across China's cities is crucial for various reasons. First, it offers insights into the social cohesiveness and potential for conflict within the nation. Countries with a wide ideological divide often face challenges in governance and social stability. As China continues to evolve, the tension between progressive and conservative ideologies could influence policy-making and social movements.
Furthermore, this ideological mapping has implications for foreign relations and economic strategies. Cities with more liberal ideologies may attract foreign investment and partnerships, while those with conservative leanings might focus on preserving traditional industries and customs.
As we look to the future, it will be fascinating to observe how these ideological trends evolve, especially with the influence of global events and technological advancements. The interplay between urbanization and ideological change will undoubtedly shape the next chapter in China's development, making it a key area of study for geographers and political scientists alike.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 23, 2025
- Views
- 48
Comments
Loading comments...