French Railways Expansion Map 1837 to 1875

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
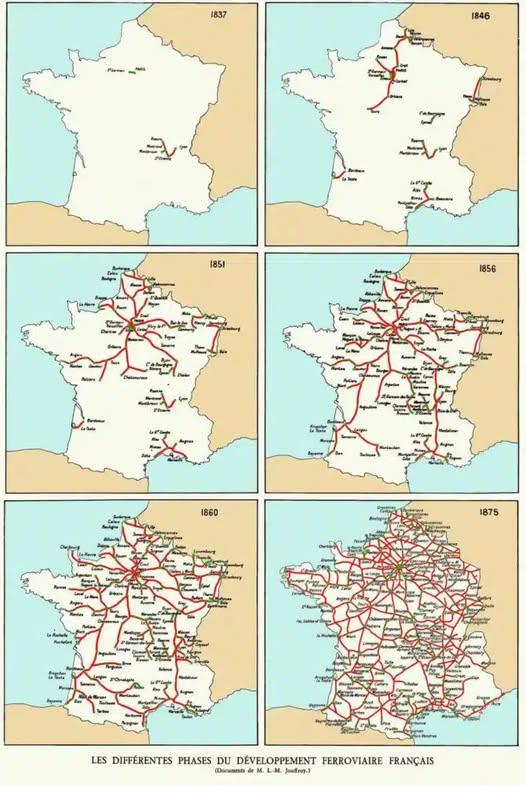
The map titled "The Rise of French Railways 1837 to 1875" provides a comprehensive visualization of the expansion of the railway network in France during a pivotal period in its history. It highlights the key railway lines, their routes, and the major cities they connected. By examining this map, one can trace the intricate web of railways that transformed not only the transport system but also the socio-economic landscape of France.
Deep Dive into French Railways
The rise of railways in France during the 19th century marked a significant turning point in the country’s transportation infrastructure. Before the advent of railways, travel and transport were predominantly reliant on horse-drawn vehicles and waterways, which were often slow and inefficient. The introduction of railways revolutionized this system, facilitating quicker movement of people and goods across vast distances.
Interestingly, the first railway line in France was opened in 1827, linking Saint-Étienne to Andrézieux, but the real boom came in the 1840s. By 1850, France had laid over 3,000 kilometers of track, and by 1870, this figure had nearly doubled to around 6,000 kilometers. This rapid expansion was not merely about laying down tracks; it was about reshaping the economy and society itself.
The French government recognized the potential of railways to stimulate economic growth, leading to increased investment and the establishment of various private companies. The map illustrates the major lines, such as the Paris-Lyon and Paris-Nord routes, which were crucial for trade and travel. Railways connected rural areas to urban centers, enabling farmers to transport their produce to markets more efficiently and allowing industries to source raw materials and distribute finished products with unprecedented speed.
Moreover, the railway system played a significant role in the urbanization of France, as cities began to grow around railway hubs. Places like Lyon, Marseille, and Lille saw a significant influx of people, changing the demographic landscape. Ever wondered how the industrial revolution was so rapid in France? Railways were key, facilitating labor movement and enabling industries to flourish in urban settings.
By 1875, the network had expanded significantly, and the map captures the essence of this transformation, reflecting the ambitious spirit of the time. The visual representation of this railway expansion not only shows the physical infrastructure but also symbolizes the broader changes in French society during the 19th century.
Regional Analysis
The map reveals distinct regional patterns in railway development. In the northern part of France, particularly around Paris, railway lines were densely packed, facilitating connections to Belgium and beyond. This area became a hub of economic activity, with quick access to markets and resources.
Conversely, the southern regions, such as Provence and the French Riviera, saw a slower development of railways. This difference can be attributed to various factors, including terrain and population density. For instance, the mountainous regions of the Alps posed significant engineering challenges, delaying railway construction. However, once completed, these lines enhanced tourism and trade in these scenic areas, showcasing how railways could bridge geographical barriers.
Interestingly, the eastern frontier saw the establishment of lines towards Germany, which was crucial for trade relations and military logistics, especially in the context of the Franco-Prussian War that was looming on the horizon. Each railway line depicted on the map tells a story of economic development, military strategy, and social change.
Significance and Impact
The rise of French railways between 1837 and 1875 had profound implications for the country and beyond. It encouraged industrial growth, facilitated urbanization, and contributed to the globalization of trade. The railway system not only connected cities but also linked different cultures and regions, creating a more unified national identity.
Today, the legacy of these railways can be seen in France’s modern transport infrastructure, where high-speed trains like the TGV have become a symbol of technological advancement. However, the historical significance of this railway expansion is not just about transportation; it reflects a broader narrative of progress, innovation, and societal change.
Looking forward, as nations grapple with climate change and the need for sustainable transportation solutions, the history of the French railway system serves as a reminder of the transformative power of infrastructure. In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, the lessons learned from the rise of railways in the 19th century remain relevant as we seek to build efficient and eco-friendly transport systems for the future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 20, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...