Historical Spread of Indian Ancestry Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
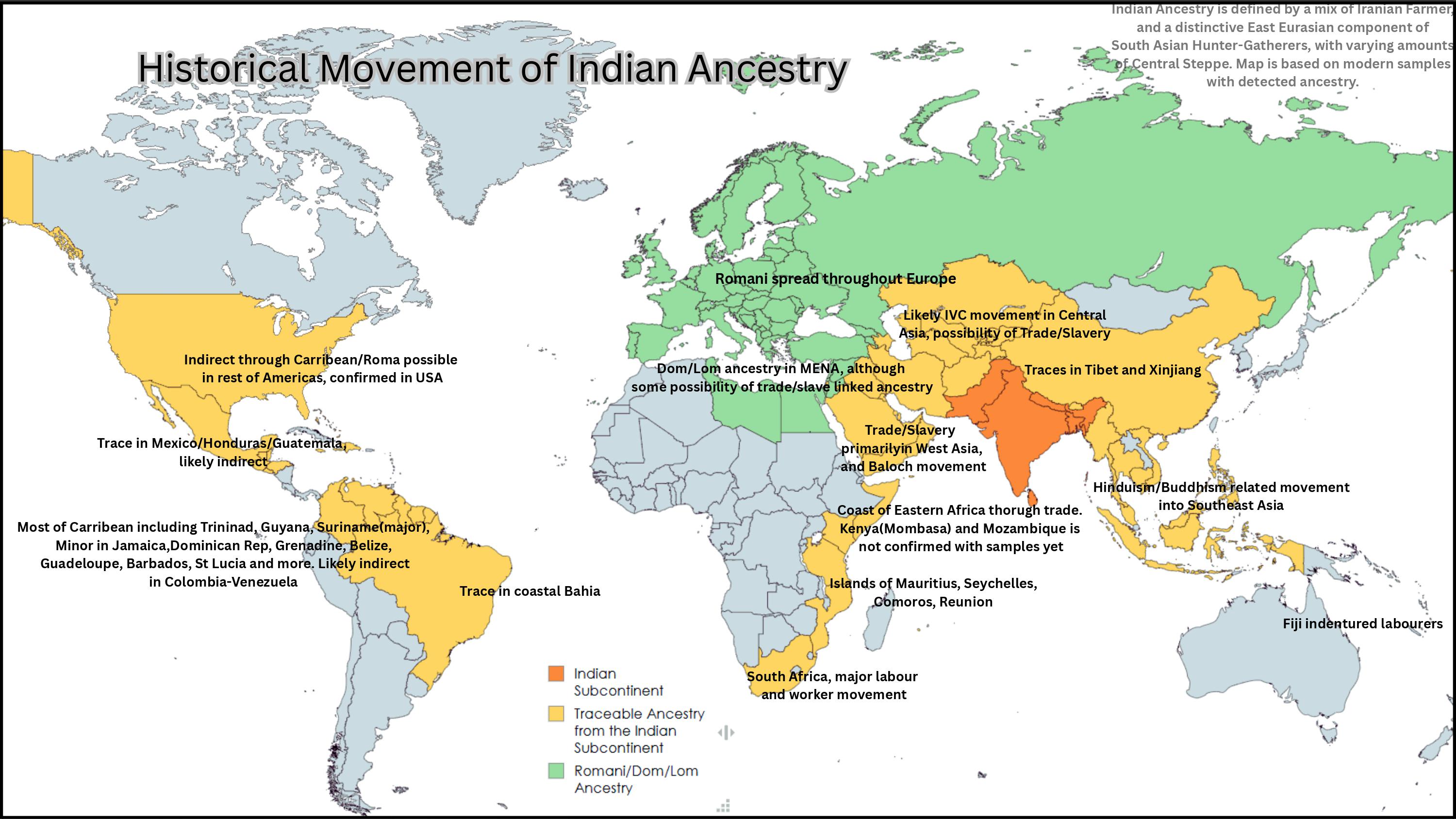
The "Historical Spread of Indian Ancestry Map" illustrates the geographic distribution of Indian ancestry across various countries and regions, suggesting the extent to which Indian ancestry has been integrated into different ethnic groups globally. The map is color-coded to indicate countries where individuals exhibit traceable amounts of Indian ancestry, emphasizing that these connections are established through historical movements rather than modern migration patterns. It’s important to note that the map does not account for isolated instances of ancestry; instead, it focuses on regions where Indian ancestry has mixed with local populations. This provides a clearer picture of how Indian ancestry has woven itself into the fabric of various societies over time.
Deep Dive into Indian Ancestry
The presence of Indian ancestry in various parts of the world can be traced back to several significant historical movements. The Indian subcontinent, with its rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and ethnicities, has a long history of maritime trade and cultural exchange that facilitated the spread of its people. For centuries, Indian traders and seafarers traveled across the Indian Ocean, reaching the shores of Africa, Southeast Asia, and even as far as Madagascar. These interactions were not merely commercial; they also led to the exchange of ideas, traditions, and genetic material.
Interestingly, the Indian diaspora is one of the largest in the world, contributing to the genetic diversity of many regions. For instance, in parts of East Africa, such as Kenya and Tanzania, there are significant Indian communities that have been established since the late 19th century. The introduction of the railway system in these regions, largely constructed by Indian laborers, further solidified this connection. The descendants of these laborers often retain cultural ties to their Indian heritage, which can be observed in their customs, cuisine, and even language.
In Southeast Asia, the historical spread of Indian ancestry is evident in countries like Malaysia and Indonesia. Indian traders, particularly during the time of the ancient maritime Silk Route, played a vital role in the socio-economic development of these regions. The Indian influence is still palpable today, with Indian festivals, cuisine, and practices being integrated into the local cultures. What’s fascinating is that in these countries, Indian ancestry is often associated with specific ethnic groups, significantly shaping their identity.
Moreover, the Indian influence is not limited to Asia and Africa. The Caribbean islands, particularly Trinidad and Tobago and Guyana, also showcase the impact of Indian ancestry. The migration of indentured laborers from India to these islands in the 19th and early 20th centuries resulted in a lasting legacy that continues to be celebrated today. Cultural festivals, such as Diwali, have become integral parts of the national fabric of these countries, reflecting a blend of Indian and local traditions.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can discern distinct patterns of Indian ancestry across different regions. In Africa, countries like Kenya and Uganda show a notable presence of Indian ancestry, primarily due to historical trade routes and the establishment of Indian settlements. Conversely, in southern Africa, while some Indian ancestry exists, it is less prevalent compared to East Africa due to different migration and settlement patterns.
In Southeast Asia, nations like Malaysia and Singapore exhibit a rich amalgamation of Indian ancestry. The Indian community in Malaysia, for example, is well-established, with roots tracing back to the Tamil migrants. This community has significantly influenced Malaysian culture, especially through cuisine and festivals.
Interestingly, Madagascar presents a unique case. While preliminary data suggests the presence of Indian ancestry, further research is needed to ascertain the extent and nature of these connections. Unlike the typical patterns observed in other regions, the Indian population in Madagascar appears to be more endogamous, meaning they have remained relatively isolated in their ancestry, which poses intriguing questions for future studies.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the historical spread of Indian ancestry is crucial for multiple reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on the interconnectedness of cultures and how historical movements have shaped modern identities. In an increasingly globalized world, recognizing these ancestral ties allows for a greater appreciation of cultural diversity.
Moreover, the implications extend beyond cultural identity. In many regions, the Indian diaspora has contributed significantly to economic development. Their entrepreneurial spirit has played a pivotal role in local economies, particularly in the retail and service sectors. Current trends indicate a growing interest in preserving cultural heritage among diaspora communities, which could lead to a resurgence of traditional practices and a strengthening of community bonds.
As we look toward the future, the study of Indian ancestry and its dispersal will likely continue to evolve, especially with advancements in genetic testing and ancestry research. The map serves as a vital tool for understanding these dynamics, inviting further exploration into the rich history shared among diverse populations across the globe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 17, 2025
- Views
- 52
Comments
Loading comments...