World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
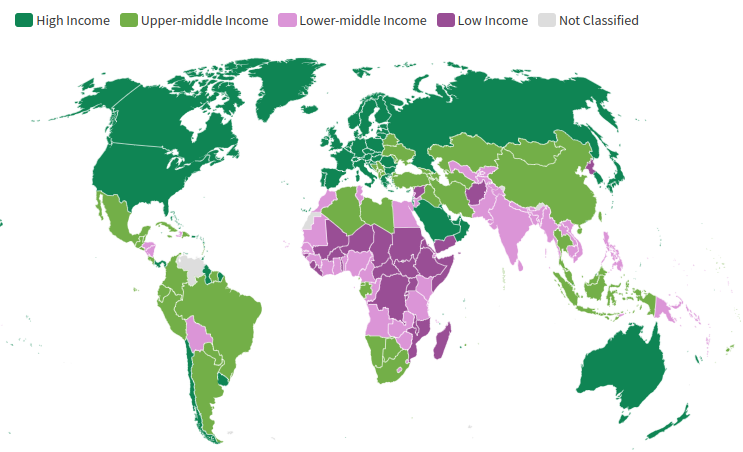
What This Map Shows
The World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level Map for 2024-2025 visually categorizes countries based on their income levels, classified into four distinct groups: low income, lower-middle income, upper-middle income, and high income. This classification serves as an essential tool for understanding global economic disparities and trends, providing insights into how different regions are progressing economically. By analyzing this map, we can explore the implications of income levels on development, health, and education across various nations.
Deep Dive into Income Levels
Income levels are crucial indicators of a country's economic health and development trajectory. The World Bank's classification system is based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita, which takes into account the average income of a country's citizens, adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP). This system helps to create a more standardized view of income across different nations, allowing for more accurate comparisons.
What’s fascinating is that income level classifications can have profound implications on a country's policies and international relations. For instance, low-income countries, often defined as those with a GNI per capita of $1,045 or less, may struggle with basic infrastructure, education, and healthcare. This can perpetuate cycles of poverty and limit opportunities for economic advancement. In contrast, high-income countries, with a GNI per capita of $13,046 or more, tend to enjoy better living standards, access to advanced healthcare, and robust educational systems.
Interestingly, the transition between these categories isn't merely a numerical change; it often reflects significant socioeconomic transformations. Countries that successfully move from lower-middle to upper-middle income status, for instance, may have invested heavily in education, infrastructure, and technology, which can drive innovation and economic growth. A prime example is Vietnam, which has seen remarkable economic development over the past few decades, moving up the income ladder through strategic reforms and investments.
Furthermore, the disparities between these income groups can highlight global challenges. Low-income countries often face issues like high unemployment rates, insufficient healthcare, and limited access to education, which can hinder their economic growth. Conversely, high-income nations may grapple with challenges such as income inequality, debt crises, and aging populations. Understanding these disparities is essential for policymakers and international organizations striving to implement effective development strategies.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the map, distinct regional patterns emerge. Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, is predominantly characterized by low-income countries, with nations such as Niger and Mozambique facing significant developmental challenges. These countries often rely on agriculture and foreign aid, which can be unstable and insufficient for long-term growth.
In contrast, regions like North America and parts of Western Europe predominantly feature high-income classifications. The United States and Canada showcase economies driven by technology and services, reflecting a high standard of living and extensive public services.
Interestingly, the Asia-Pacific region presents a mix of classifications. Countries like China and India, which are classified as upper-middle income, exhibit rapid economic growth but also significant inequality within their populations. This stark contrast within the region shows how diverse economic landscapes can be, even among neighboring countries.
Another noteworthy example is Latin America, where countries like Brazil and Argentina fall into the upper-middle income category, while others, like Haiti, remain low-income. This variation can be attributed to historical economic policies, political stability, and access to natural resources.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the World Bank's income level classifications is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it helps international organizations and governments tailor their development assistance programs to the specific needs of each country. By recognizing the challenges faced by low-income nations, initiatives can be designed to address fundamental issues like healthcare access, education, and infrastructure development.
Moreover, as the global economy evolves, these classifications can shift, reflecting changing dynamics. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted economies worldwide, potentially altering income classifications in the upcoming years. Countries that previously experienced growth may find themselves struggling, while others could seize the opportunity to advance through innovative solutions and economic diversification.
In conclusion, the World Bank Country Classifications by Income Level Map for 2024-2025 is more than just a tool for categorizing nations; it's a lens through which we can examine global economic disparities and the interconnectedness of our world. By understanding these classifications, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for countries at different stages of economic development.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 12, 2025
- Views
- 198
Comments
Loading comments...