Literacy Rates in Romania 1930 Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
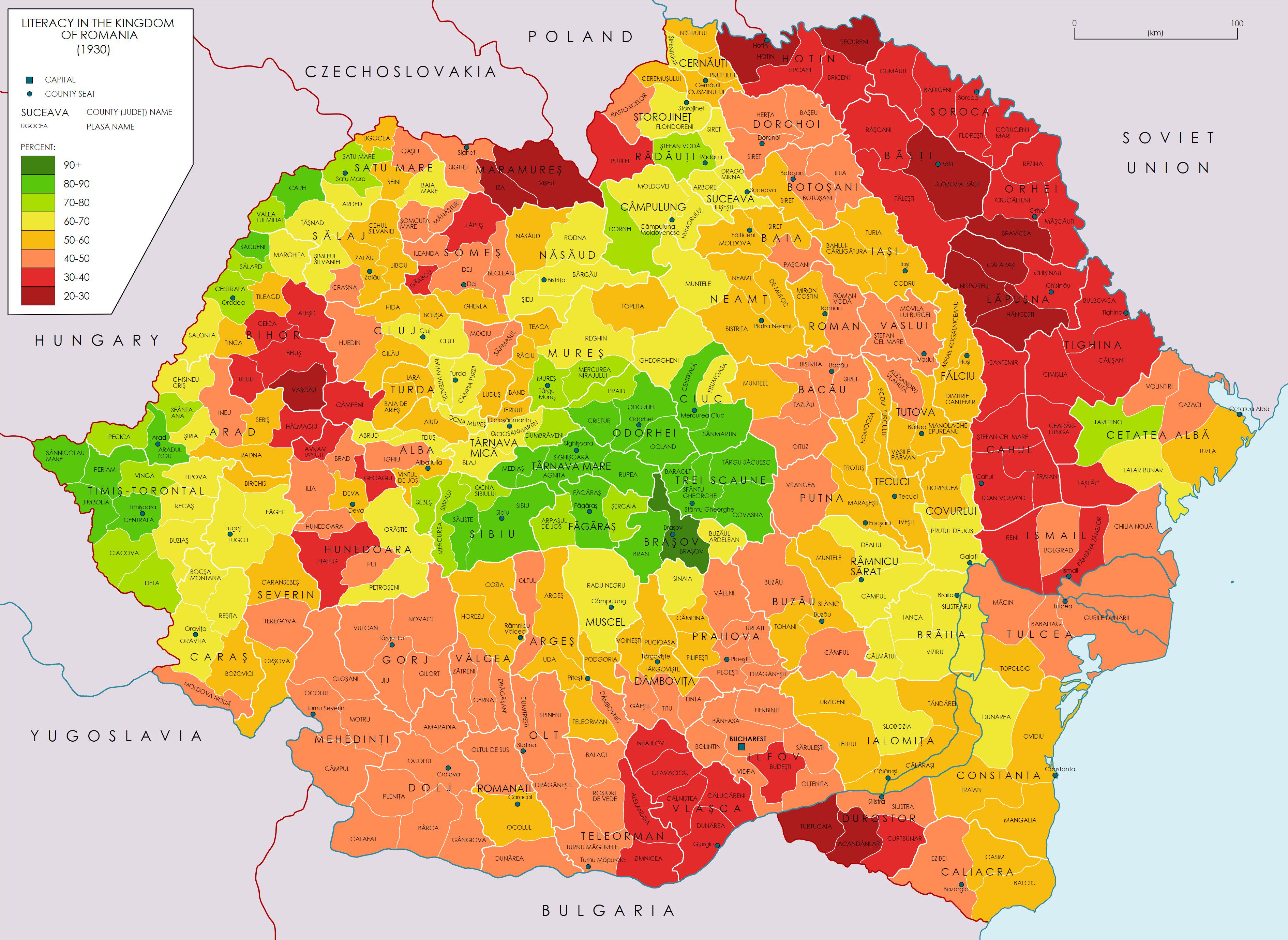
The map titled 'Literacy Rates in the Kingdom of Romania in 1930' provides a visual representation of literacy levels across different regions of Romania during a pivotal time in its history. It highlights the disparities in literacy, revealing how education was distributed throughout the kingdom. This visualization not only sheds light on the educational landscape of Romania in the early 20th century but also serves as a historical reference to understand the nation’s socio-economic development at that time.
Deep Dive into Literacy in Romania
Literacy is a foundational pillar of societal progress, influencing everything from economic development to civic participation. In 1930, Romania was a kingdom that had just emerged from the turmoil of World War I and was grappling with the challenges of modernization. The literacy rate during this period was a critical indicator of the nation's educational advancements and societal structure.
At the onset of the 20th century, Romania's literacy rates were relatively low, particularly in rural areas. The country was primarily agrarian, and access to education was limited, especially for women and marginalized communities. However, by 1930, there had been concerted efforts to improve education, resulting in varying literacy rates across different regions.
Interestingly, urban areas like Bucharest and Cluj saw significantly higher literacy rates compared to rural regions. For instance, Bucharest boasted literacy rates above 80%, reflecting the concentration of educational institutions and economic opportunities. In contrast, more isolated areas such as Maramureș and parts of Moldavia struggled with rates as low as 30-40%. This was often due to factors such as economic limitations, cultural attitudes towards education, and the availability of schools.
Furthermore, the map highlights the impact of socioeconomic status on literacy. Wealthier regions were more likely to have well-funded schools and better-trained teachers, which contributed to higher literacy rates. Conversely, poorer areas faced challenges such as inadequate infrastructure and a lack of resources. This divide illustrates how access to education is not just a matter of policy but is deeply intertwined with economic and social factors.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map further reveals fascinating regional patterns. For example, Transylvania, with its mixed ethnic population, showed varying literacy rates among different communities. The Saxon and Hungarian populations often had higher literacy rates compared to the Romanian-speaking populace, highlighting the influence of cultural heritage on educational attainment.
In contrast, the Dobruja region, which had a significant population of ethnic minorities, exhibited lower literacy levels, which can be attributed to both economic hardship and the effects of World War I, which had disrupted educational systems.
Another notable aspect is the role of gender in literacy rates. The map might not explicitly detail gender differences, but historical data indicates that women in urban areas had better access to education than their rural counterparts. While overall literacy rates were improving, the gap between male and female literacy rates persisted, particularly in the countryside where traditional roles typically placed less value on female education.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the literacy rates of Romania in 1930 is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insight into the challenges the country faced as it was transitioning from a largely agrarian society to a more modern state. Education plays a vital role in this transformation, and the disparities highlighted by the map underscore the complexities involved in achieving widespread literacy.
Today, we can see echoes of these historical patterns in contemporary Romania. Although literacy rates have significantly improved, regional disparities still exist, particularly in rural areas. Addressing these gaps remains a pressing issue for policymakers aiming to enhance educational access and quality across the nation.
Moreover, this historical perspective on literacy can inform current discussions on educational reforms and highlight the importance of equitable access to resources. As we look forward, promoting literacy remains essential, not just for individual empowerment but for the overall development of society as a whole. Have you ever wondered how much education shapes a nation’s future? It’s clear that the roots of today's educational landscape can often be traced back to historical events and trends like those captured in this map.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 8, 2025
- Views
- 94
Comments
Loading comments...