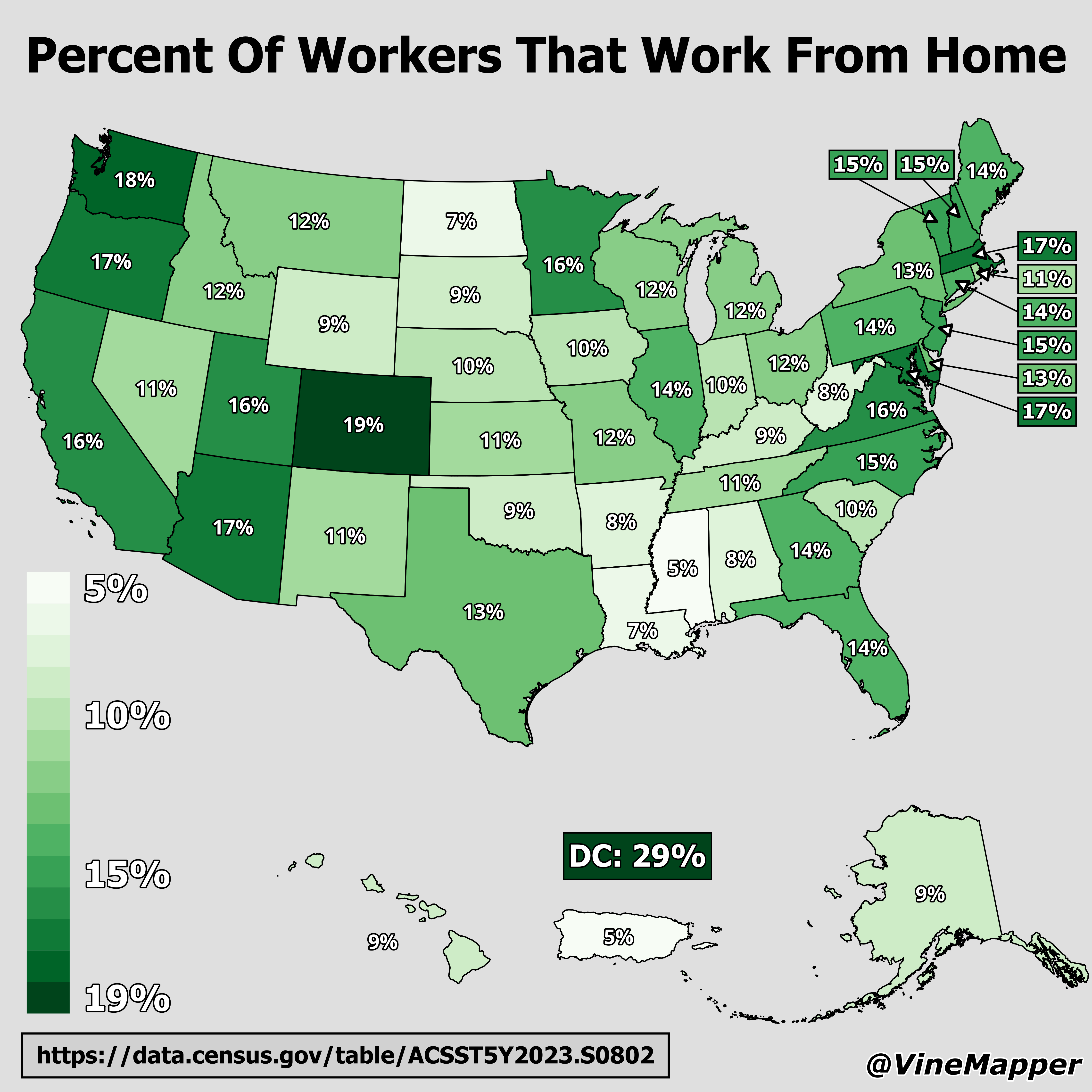
Percent of Workers That Work From Home Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Percent of Workers That Work From Home" map provides a visual representation of the varying rates at which employees across different regions are engaging in remote work. It highlights the percentage of the workforce that has transitioned to home-based work settings, reflecting a significant shift in employment trends influenced by technology, economic factors, and recent global events. This map serves as a crucial indicator of how workplace dynamics are evolving in different geographical contexts, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the acceptance of remote work across many sectors.
Deep Dive into Remote Work Trends
Working from home is not just a trend; it has become a transformative aspect of modern employment. In recent years, particularly since the onset of the pandemic, the concept of remote work has gained traction, fundamentally altering how companies operate and how employees balance their work and personal lives. Interestingly, studies show that remote work can increase productivity, reduce overhead costs for businesses, and improve work-life balance for employees.
However, the adoption of remote work is not uniform across the globe. Factors such as industry type, company culture, and regional economic conditions play essential roles in determining the percentage of workers who can work from home. For instance, sectors like information technology, finance, and professional services exhibit higher percentages of remote work capability compared to industries like manufacturing and healthcare, where physical presence is often required.
According to recent statistics, about 30% of the workforce in urban areas has shifted to remote work roles, while rural areas lag behind with percentages often dropping below 20%. This discrepancy raises questions about access to technology and the infrastructure needed to support remote work, such as reliable internet connectivity and adequate home office spaces.
Moreover, demographics also influence remote work trends. Younger workers, particularly those in the millennial and Gen Z age groups, are more inclined toward remote work options than older generations. This inclination not only reflects their adaptability to technology but also their desire for flexibility and autonomy in their jobs.
As the workforce continues to evolve, the implications of these trends are far-reaching. Companies are now re-evaluating their real estate needs, leading to a potential decrease in demand for office spaces. Furthermore, as remote work becomes a more permanent fixture, organizations might need to implement new management strategies and policies to ensure productivity and employee engagement.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map reveals fascinating regional disparities in remote work adoption. For instance, metropolitan areas like San Francisco and New York City showcase high percentages of remote workers, often exceeding 40%. These cities are home to numerous tech companies and startups that champion flexible work arrangements, thus fostering an environment conducive to remote work.
Conversely, states with economies heavily reliant on traditional industries, such as manufacturing or agriculture, display lower percentages. For example, states like Indiana and Arkansas show remote work rates closer to 15-20%. It's clear that the economic base of a region significantly influences the feasibility of working from home.
Interestingly, regions that have invested in digital infrastructure and connectivity, such as parts of the Midwest and the Northeast, have seen a more considerable increase in remote work capabilities. In contrast, areas with limited internet access or a lack of tech-oriented businesses are still grappling with the transition. This highlights a digital divide that could have long-lasting implications for economic equality.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the dynamics of remote work is crucial for various stakeholders, including policymakers, businesses, and educators. The rise of remote work has implications for urban planning, labor laws, and economic development strategies. As cities adapt to these changes, they must consider how to support both remote and in-office workers effectively.
Moreover, this shift toward remote work is likely to influence future job training programs. With more positions requiring digital skills, educational institutions will need to pivot to meet the demands of a digitally-savvy workforce.
Looking ahead, projections indicate that remote work will remain a significant part of the employment landscape. While the pandemic accelerated its adoption, the long-term benefits of flexibility and accessibility suggest that many companies and employees will continue to embrace this model. Have you noticed how your own workplace has adapted to these changes? It’s a fascinating time in the world of work, and the ongoing evolution will certainly shape our economies and societies for years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...