Genome Ancestry Clusters of Present-Day Europeans Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
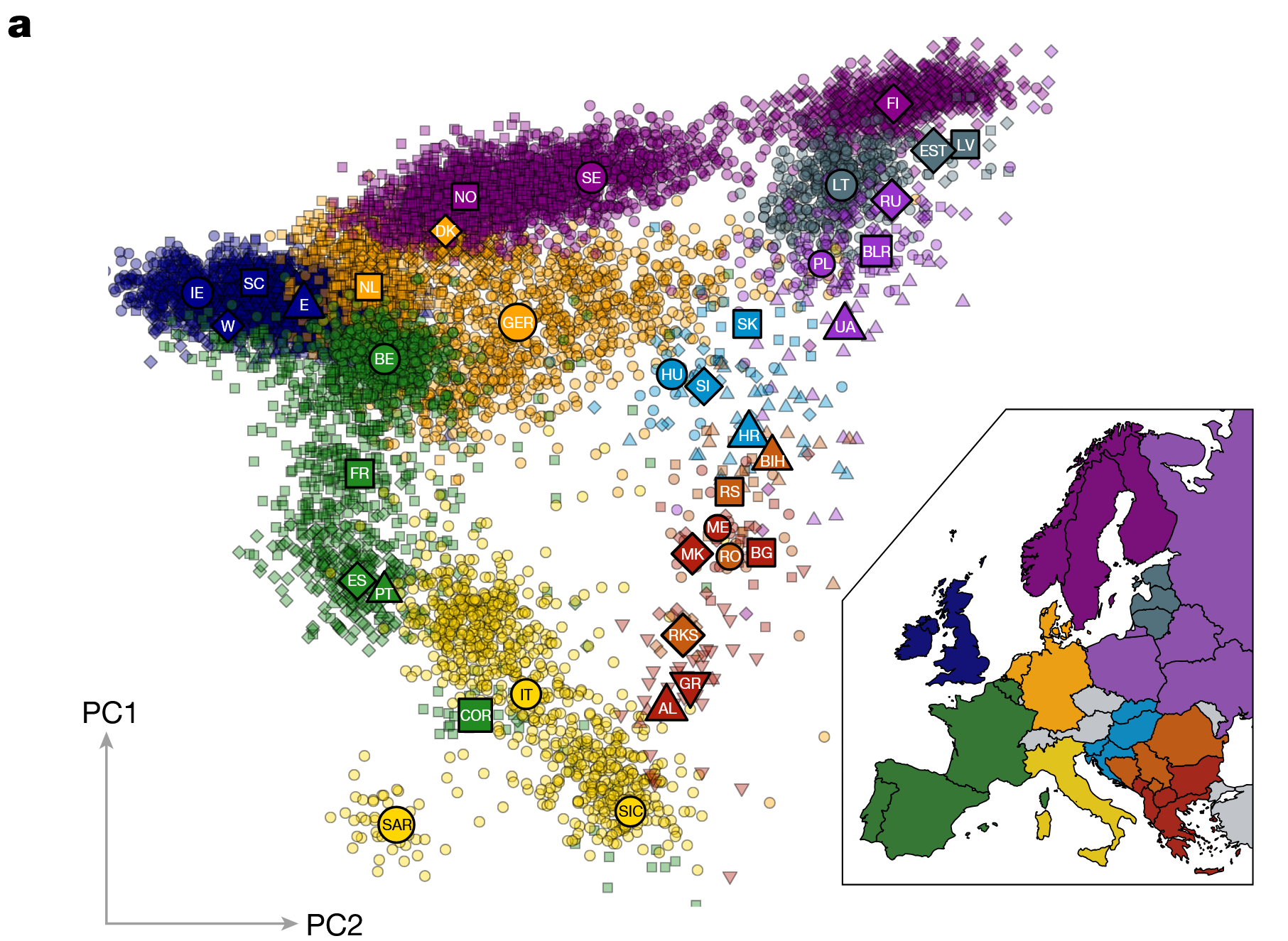
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Genome Ancestry Clusters of Present-Day Europeans" utilizes principal component analysis (PCA) to illustrate the genetic diversity and ancestry clusters across Europe. It effectively depicts how various populations within Europe have distinct genetic markers that reflect their historical migrations and interrelations. PCA is a statistical technique that reduces complex data sets, making it easier to visualize and understand genetic relationships among different populations. This map highlights how ancestry influences modern demographics, revealing a rich tapestry of genetic heritage that has developed over centuries.
Deep Dive into Genetic Ancestry in Europe
Genetic ancestry is an intriguing subject that unravels the story of human migration and adaptation over millennia. Europe, with its long history of movement and settlement, showcases a remarkable genetic mosaic. Scholars have identified several major ancestry clusters among Europeans, often linked to historical events such as the Neolithic agricultural revolution, Indo-European migrations, and more recent population movements due to trade and conflicts.
The map is particularly revealing in its representation of genetic clusters. For instance, the Northern Europeans, including populations from Scandinavia, display a unique genetic signature characterized by high frequencies of certain haplogroups. Interestingly, this cluster indicates a strong historical continuity, reflecting how relatively isolated these populations have remained compared to their southern counterparts.
In contrast, Southern Europeans, such as Italians and Greeks, show a more diverse genetic background influenced by various waves of migration, including ancient Mediterranean traders and more recent movements from the Middle East and North Africa. This genetic complexity is reflected in the map, which indicates a mix of ancestry that corresponds to historical trade routes and cultural exchanges.
Moreover, the map reveals the significant impact of the Roman Empire on genetic lineage. Regions that were once part of the empire often show a blend of genetic influences from various conquered populations, creating a rich genetic heritage. The Iberian Peninsula, for example, reveals a fascinating mix of North African, Iberian, and even Celtic ancestry due to its history of conquests and colonization.
Understanding these genetic clusters not only illuminates the historical narrative of human populations but also has implications for health, disease susceptibility, and even social identity in modern Europe. Genetic predispositions linked to specific clusters can influence how populations respond to certain health challenges, making this map an essential tool for public health planning and research.
Regional Analysis
When examining Europe through the lens of genetic ancestry, regional differences become apparent. In Northern Europe, countries like Finland, Sweden, and Norway exhibit genetic clusters that are relatively homogeneous due to their geographical isolation and historical population structures. For example, the Sami people of Northern Scandinavia represent a unique genetic lineage that has been preserved over thousands of years, distinct from the surrounding populations.
Moving southward, the genetic landscape becomes more diverse. Central European nations such as Germany and Poland show a blend of Eastern and Western European genetic markers, reflecting their historical interactions and migrations. Interestingly, historical events like the migration of the Slavs into Central Europe have left lasting genetic traces, as seen in the genetic makeup of contemporary populations.
In contrast, the Balkans present a complex genetic tapestry, with influences from various empires, including the Ottoman and Austro-Hungarian. The map clearly delineates these intricacies, showcasing how the region's tumultuous history has shaped its genetic landscape. Countries like Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina exhibit a mix of South Slavic and other genetic influences, highlighting the region's historical migrations.
Significance and Impact
The significance of understanding genetic ancestry clusters in present-day Europeans extends beyond academic interest; it impacts public health, social cohesion, and identity. For instance, as genetic research progresses, it can lead to breakthroughs in disease prevention and treatment tailored to specific populations based on their genetic predispositions. Furthermore, knowledge of ancestry can help address social issues related to identity and heritage, fostering a greater appreciation of Europe’s complex historical narrative.
Interestingly, as globalization continues to blend cultural and genetic lines, the future of European genetic ancestry may evolve dramatically. With increased migration and intermarriage, the distinct clusters might become less pronounced, leading to a more homogenized genetic makeup. However, the historical and genetic diversity that this map represents will remain a vital part of understanding Europe's past and present. As we move forward, the interplay between genetic heritage and contemporary identity will surely continue to shape the social landscape of Europe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 98
Comments
Loading comments...