Current State of Mali War Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
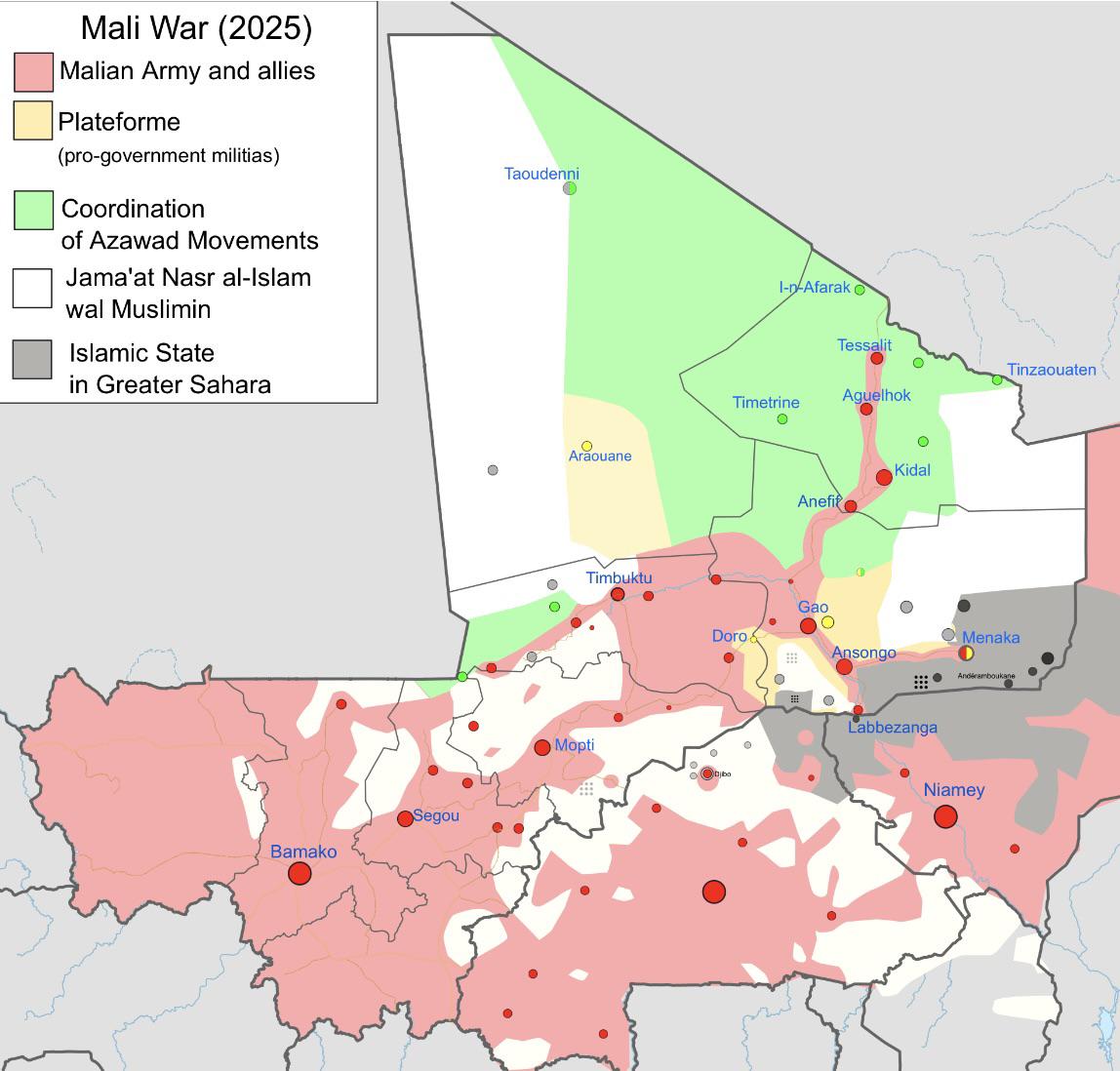
The visualization titled "The Current State of Mali War (c. August 2025)" provides a snapshot of the ongoing conflict in Mali as it stands in mid-2025. It highlights key areas of military activity, territorial control, and the influence of various armed groups in the region. The map delineates zones held by government forces, areas controlled by insurgent factions, and regions where clashes are frequent, particularly those associated with Al-Qaeda and other extremist groups.
Transitioning from this visualization, it’s crucial to understand the broader context of the conflict in Mali, which has been a focal point of instability in West Africa. The war is not merely a local issue but represents a complex interplay of factors involving historical grievances, ethnic tensions, and global jihadist movements.
Deep Dive into the Mali Conflict
The conflict in Mali can be traced back to a variety of causes, including the post-colonial legacy, ethnic divisions, and the fallout from the Arab Spring. The Tuareg people, a nomadic ethnic group in the north, have long sought greater autonomy and recognition. In 2012, a rebellion by Tuareg separatists in the northern regions escalated into a full-blown conflict as various jihadist groups seized control. What’s fascinating is how these local grievances have been exploited by larger international terrorist networks, including Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM).
Interestingly, the map shows not only the current territorial divisions but also the strategic importance of key cities like Gao and Timbuktu. These areas have become battlegrounds due to their historical significance and economic resources. Mali’s vast desert landscapes and limited infrastructure present challenges for governance and security, allowing insurgent groups to thrive.
As of 2025, the conflict remains fluid, with shifting alliances and ongoing military operations. The Malian army, supported by international forces from France and the United Nations, continues to engage in counter-insurgency operations. However, despite these efforts, the presence of extremist groups has not diminished significantly, leading to a persistent state of insecurity.
Statistics paint a stark picture: thousands of civilians have been displaced due to the violence, with the United Nations reporting that the humanitarian crisis is at an all-time high. The number of displaced persons reached over 300,000, highlighting the dire situation for those caught in the crossfire. Moreover, the economic ramifications are severe, as agricultural production in conflict zones plummets, leading to food insecurity and poverty.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map further, we can differentiate between the northern, central, and southern regions of Mali. The north, primarily dominated by the Tuareg and various jihadist factions, is characterized by lawlessness and frequent skirmishes. Cities like Kidal are not just insurgent strongholds but also hotspots for international attention due to their proximity to the Sahara, which is often used for smuggling and trafficking.
In the central regions, the conflict has taken on a new dimension, with clashes often occurring between ethnic communities, such as the Dogon and Fulani. This intercommunal violence complicates the security landscape, as traditional grievances are exacerbated by the presence of armed groups. Interestingly, while the government focuses on combating terrorism, it often overlooks these local conflicts, which can lead to more significant instability.
The southern region, while relatively more secure, is not immune to the effects of the war. This area serves as a refuge for many fleeing violence, yet it also faces challenges related to governance and resource distribution. The influx of internally displaced persons strains local resources and heightens tensions, showcasing the interconnectedness of the conflict throughout the country.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the current state of the Mali war is crucial not only for grasping the dynamics of West African geopolitics but also for recognizing the implications of global counterterrorism strategies. The presence of Al-Qaeda and affiliated groups in Mali poses a threat not just regionally but globally, as these networks can extend their operations across borders, influencing security in neighboring countries like Niger and Burkina Faso.
Moreover, the humanitarian impact of the conflict cannot be overstated. The ongoing violence has led to a severe humanitarian crisis, with millions in need of assistance. The international community faces a dilemma: how to effectively intervene without exacerbating the situation. As of 2025, the future remains uncertain, with the potential for both escalation and resolution hanging in the balance.
In conclusion, the map of the current state of the Mali war serves as a critical reminder of the complexities involved in addressing modern conflicts. By understanding the geographical and socio-political intricacies, we gain insight into the challenges facing not just Mali, but the broader Sahel region. The stakes are high, and the battle for stability and peace continues.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 1, 2025
- Views
- 150
Comments
Loading comments...