Wolf Population in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
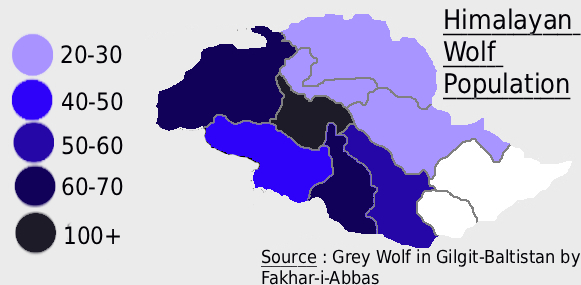
What This Map Shows
This map provides a detailed visualization of the wolf population across Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. By showcasing the distribution of wolves in this mountainous region, the map gives us insight into their habitat, population density, and the potential factors influencing their numbers. The stark geographical features of Gilgit-Baltistan, including its rugged mountains and diverse ecosystems, play a crucial role in shaping the lives of its wildlife, particularly apex predators like wolves.
Deep Dive into Wolf Population in Gilgit-Baltistan
Wolves are not just animals; they are integral components of the ecosystems they inhabit. In Gilgit-Baltistan, a region characterized by its rich biodiversity, the wolf population thrives primarily due to the availability of prey and suitable habitats. Wolves in this area are primarily of the species Canis lupus, which has adapted to the harsh conditions of the Himalayas and Karakoram ranges.
Interestingly, the wolf population in Gilgit-Baltistan is often linked to the presence of livestock. Local pastoral communities frequently raise sheep and goats, which serve as the main prey for wolves. However, this relationship can lead to conflicts, as wolves may target livestock, prompting farmers to take measures to protect their herds. It’s a classic case of wildlife conservation versus agricultural needs, raising questions about sustainable coexistence.
The current population estimates for wolves in Gilgit-Baltistan suggest a healthy number, but these figures can fluctuate due to various factors. Predation pressures, habitat availability, and human activity all impact their numbers. According to studies, the wolf population density can vary significantly depending on the region within Gilgit-Baltistan. For instance, areas with less human encroachment, such as the remote valleys of Naltar and Hunza, tend to support larger wolf packs compared to more populated areas.
Wolves are social creatures, often living and hunting in packs that can range from 2 to over 10 individuals. Their social structure is key to their survival, allowing them to take down larger prey and defend their territory. The dynamics of these packs can be influenced by environmental conditions, prey availability, and human interactions. Interestingly, wolf packs in Gilgit-Baltistan have been observed to communicate through a series of howls, which not only serve to strengthen social bonds but also help in establishing territory.
Moreover, the geographical features of Gilgit-Baltistan, with its high altitudes and diverse habitats ranging from alpine meadows to rocky terrains, provide wolves with the necessary resources for hunting and shelter. These unique environmental conditions make the region a significant area for wolf conservation efforts. Conservationists emphasize the importance of preserving natural habitats to maintain the health of the wolf population, which in turn supports the overall ecological balance of the area.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the wolf population by specific regions in Gilgit-Baltistan reveals intriguing patterns. For instance, the northern regions, particularly around the Khunjerab Pass, have reported higher wolf sightings due to the abundant prey and less human interference. Conversely, areas closer to major settlements, like Skardu, show a decline in wolf numbers. This decline can be attributed to habitat destruction, increasing livestock farming, and direct human-wildlife conflicts.
Interestingly, the valleys of Ghizer and Gupis are also notable for their wolf populations, with reports indicating a healthy number of wolf packs thriving there. The geographical isolation of these valleys helps in minimizing human-wildlife conflicts, allowing wolves to flourish. While the population in these areas remains stable, the integration of community-based conservation initiatives is crucial to ensure these wolves continue to thrive.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the wolf population in Gilgit-Baltistan is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for biodiversity conservation and local livelihoods. Wolves play a critical role in regulating prey populations, which in turn affects the entire ecosystem. A balanced predator-prey relationship helps maintain the health of the grasslands and forests, preventing overgrazing and promoting biodiversity.
However, as human populations grow and expand into rural areas, the future of wolves in Gilgit-Baltistan hangs in the balance. Conservation efforts are essential to mitigate conflicts between wolves and livestock, helping local communities understand the ecological importance of wolves. This could involve implementing protective measures for livestock, promoting alternative livelihoods, or even establishing wolf reserves.
In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the need for sustainable practices that benefit both wildlife and human populations. It’s a delicate dance of coexistence, but with community engagement and education, there’s hope for the future of wolves in this majestic region. As we look ahead, monitoring the wolf population and its interactions with humans will be critical to ensuring these magnificent creatures continue to roam the wild landscapes of Gilgit-Baltistan.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 31, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...