EU Sanctions Countries Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
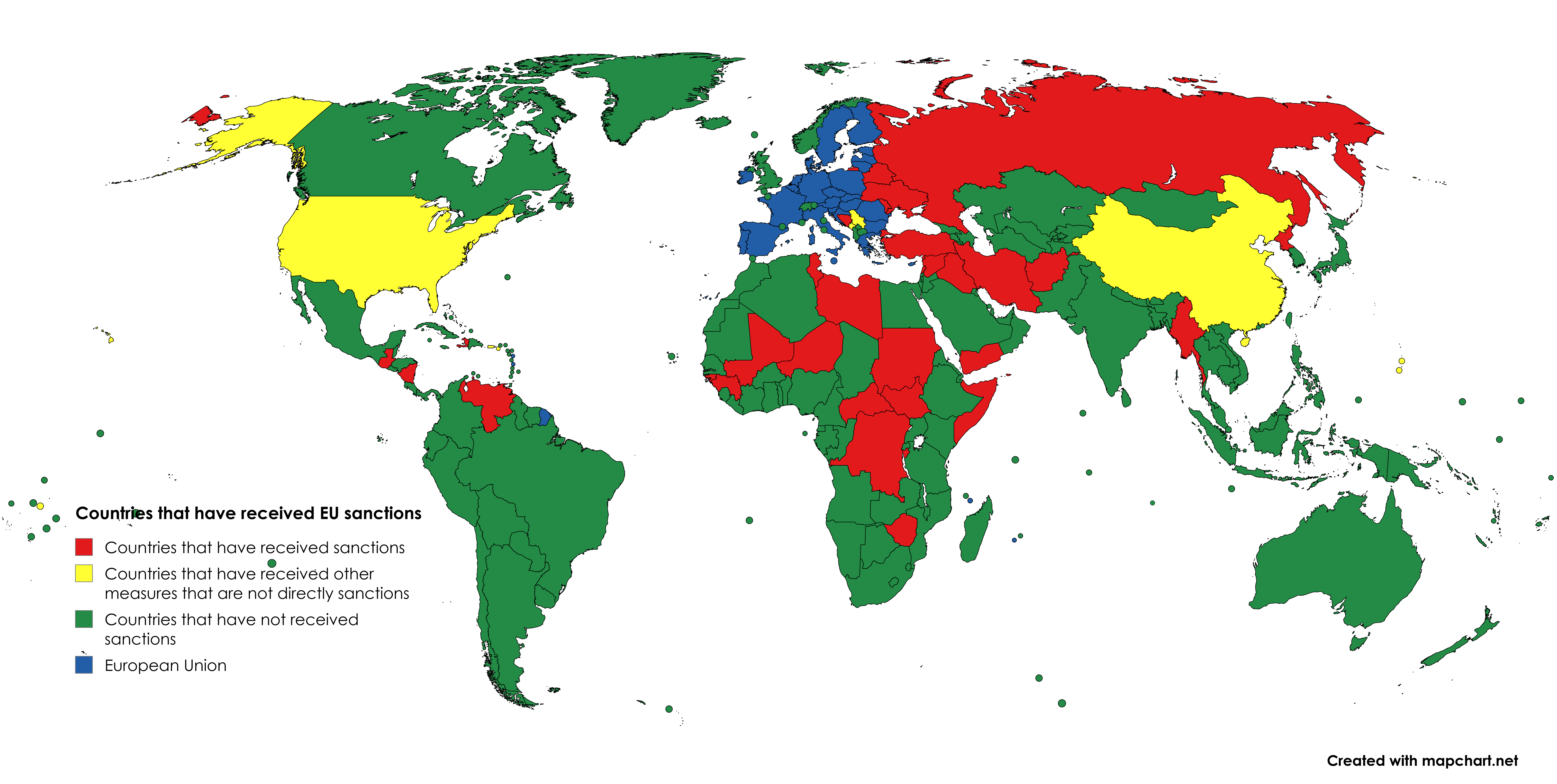
What This Map Shows
The "Countries that have received EU sanctions" map provides a comprehensive visual representation of nations that have faced economic or political restrictive measures imposed by the European Union. This visualization highlights the geographical distribution of sanctions, focusing on the specific countries that have been targets of the EU's foreign policy decisions. As we delve deeper into the topic, it becomes crucial to understand the dynamics behind these sanctions and their implications on global relations.
Deep Dive into EU Sanctions
The European Union employs sanctions as a foreign policy tool to achieve specific goals, often aimed at promoting peace, security, and democracy or responding to violations of international law. These sanctions can vary widely, encompassing economic measures like trade restrictions, asset freezes, and travel bans on individuals. The reasons behind these sanctions can stem from human rights abuses, military aggression, or political instability in the targeted countries.
Interestingly, in recent years, the number of countries that have faced EU sanctions has increased significantly. As of 2023, over 30 countries have been impacted, reflecting a growing trend of the EU using sanctions as a means of exerting influence on global affairs. For example, Russia has faced extensive sanctions due to its annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its ongoing military actions in Ukraine. These sanctions have not only targeted specific individuals but have also had far-reaching effects on the Russian economy, leading to a significant downturn and international isolation.
Another notable example is Belarus, which has been under EU sanctions following the controversial presidential elections in 2020 and the subsequent crackdown on protests. The EU has used sanctions against Belarusian officials and entities to pressure the government to respect democratic principles and human rights.
Moreover, the EU has imposed sanctions on countries like Iran and North Korea as part of broader efforts to address issues such as nuclear proliferation and terrorism. These sanctions often involve intricate negotiations and collaborations with other nations, highlighting the complexity of international relations and the interconnectedness of global security.
In terms of statistics, the economic impact of these sanctions can be profound. For instance, estimates suggest that sanctions against Russia have led to a contraction of its GDP by approximately 3% annually since their imposition. This economic strain illustrates how such measures can influence not only the target nation but also have ripple effects on global markets.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes apparent that the geographic distribution of EU sanctions is not uniform. Europe itself stands at the forefront, with countries like Russia and Belarus prominently affected. However, the sanctions extend beyond Europe’s borders, reaching regions such as the Middle East and Asia.
In the Middle East, Iran has been a significant target for EU sanctions due to concerns over its nuclear program. These sanctions have had a considerable impact on Iran's economy, leading to high inflation rates and a decrease in oil exports, which are crucial for its economic stability. Interestingly, despite the sanctions, Iran has sought to strengthen ties with other nations like China and Russia, demonstrating how geopolitical alliances can shift in response to such external pressures.
In Asia, North Korea remains a focal point for EU sanctions aimed at curbing its nuclear ambitions. The EU's approach to North Korea has been multifaceted, involving not just sanctions but also diplomatic efforts to encourage dialogue and denuclearization. The situation in North Korea presents a unique case, as the regime’s isolation has led to severe humanitarian issues, raising questions about the effectiveness of sanctions as a means of achieving policy goals.
The African continent also features in the EU sanctions landscape, with countries like Libya and Sudan facing restrictions. These sanctions often pertain to issues like armed conflict and human rights violations, showcasing the EU’s commitment to promoting stability and governance in volatile regions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the implications of EU sanctions is crucial for grasping the current geopolitical climate. Sanctions can serve as powerful tools for promoting change; however, they can also lead to unintended consequences, such as humanitarian crises or the strengthening of authoritarian regimes that may use external threats to consolidate power.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the impact of sanctions reverberates beyond the targeted nations, affecting global trade, security alliances, and even domestic policies in EU member states. Interestingly, the effectiveness of sanctions is often debated, with some arguing that they can lead to increased hostility rather than compliance.
Looking ahead, the landscape of international relations is likely to continue evolving, with sanctions remaining a key component of the EU’s foreign policy strategy. The ongoing conflicts in regions like Ukraine and the Middle East suggest that the EU will need to navigate a complex web of alliances and adversities, adapting its approaches to address emerging challenges.
In conclusion, the map of countries that have received EU sanctions is not just a visual representation of geopolitical tensions; it reflects the intricate interplay of economics, diplomacy, and international law that shapes our world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 30, 2025
- Views
- 70
Comments
Loading comments...