Thuringian Kingdom Map in 500 A.D.

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
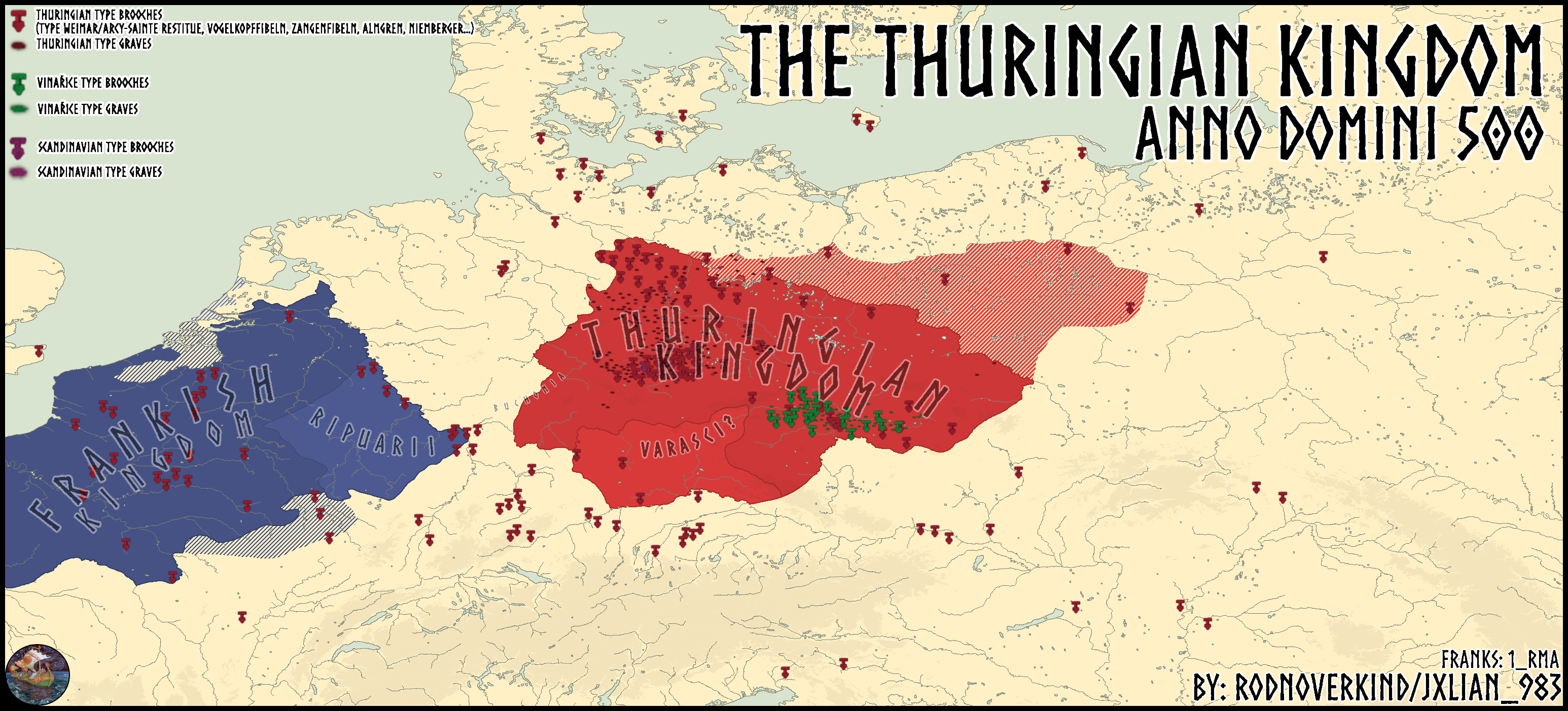
The map titled "The Thuringian Kingdom in 500 A.D." provides a detailed geographical representation of the Thuringian Kingdom during the early Middle Ages. This visualization highlights the territorial extent, key settlements, and geographical features of the kingdom, which was located in what is now central Germany. The Thuringian Kingdom was significant during this period as it served as a vital cultural and political entity among various Germanic tribes.
Now, let’s delve into the actual topic: the Thuringian Kingdom itself.
Deep Dive into the Thuringian Kingdom
The Thuringian Kingdom, known as "Thuringia," was one of the many Germanic kingdoms that emerged in the wake of the decline of the Western Roman Empire. By 500 A.D., this kingdom had established its influence in a region characterized by dense forests, river valleys, and fertile plains. Interestingly, the Thuringians were known for their agricultural prowess, utilizing the fertile soil of the Werra and Unstrut river valleys for farming. This agrarian lifestyle allowed for population growth and the development of settlements.
The Thuringian Kingdom was distinct for its tribal structure, comprising various clans that governed under a central king. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Thuringians practiced a mix of paganism and early Christian beliefs, which influenced their cultural practices and social organization. The map illustrates key settlements such as the capital city of "Hohenburg," which served as a political and administrative center. The existence of fortified sites indicates a society that valued security and defense, particularly as neighboring kingdoms posed threats.
Moreover, the Thuringians were known for their craftsmanship, especially in metalwork and textiles. This craftsmanship played a crucial role in trade, as the kingdom engaged in commerce with neighboring tribes and regions. Interestingly, the maps of trade routes from this period often show connections to significant hubs, indicating the Thuringians’ role as middlemen in the exchange of goods.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the Thuringian Kingdom as depicted on the map, we can see distinct regional variations. The western part of the kingdom, bordered by the Rhine River, was more influenced by Roman culture due to proximity. This area was bustling with trade, showcasing a blend of Roman and Germanic customs. In contrast, the eastern regions were more isolated and retained a strong connection to traditional Germanic practices, evident in their settlements and burial customs.
For instance, the city of "Erfurt," located centrally within the kingdom, functioned as a cultural melting pot. This city became a significant location for both trade and governance, exemplifying the intersection of various influences. On the other hand, the more northern areas, such as the region near "Saale River," displayed a rugged landscape with fewer settlements, indicating a less urbanized lifestyle.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Thuringian Kingdom and its geographical context is crucial for grasping the broader narrative of early medieval Europe. The dynamics within this kingdom illustrate the complexities of tribal governance, cultural exchanges, and the transition from paganism to Christianity. The Thuringians played a pivotal role in the gradual formation of what would eventually become the German nation-state.
Moreover, the significance of the Thuringian Kingdom continues to resonate today. The region of Thuringia remains a cultural hub in modern Germany, known for its historical sites, including the Wartburg Castle, which ties back to the legacy of the kingdom. Current trends in regional identity and historical research often draw parallels to this early kingdom, emphasizing the importance of understanding our roots. As we study these ancient maps, we can appreciate how geography shaped human societies and continues to influence us today.
In conclusion, the map of the Thuringian Kingdom in 500 A.D. is not just a historical artifact; it serves as a window into a complex society that thrived in a transformative era. Have you ever considered how geography influences culture? The Thuringians are a testament to that enduring relationship, showcasing how land shapes lives, traditions, and identities.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 30, 2025
- Views
- 82
Comments
Loading comments...