EU Member States Area Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
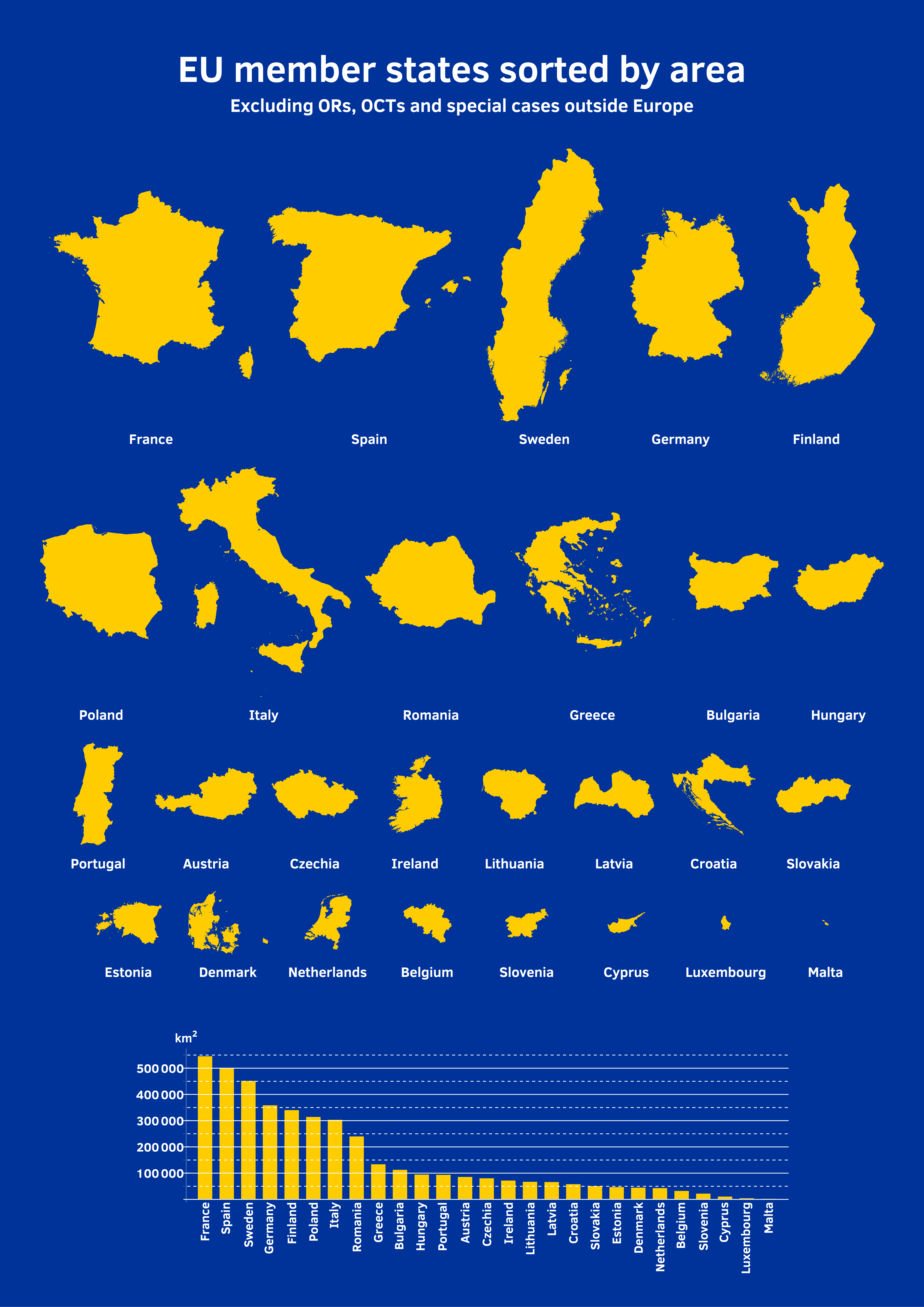
The visualization titled "Member States of the European Union, to Scale and Sorted by Area" provides a fascinating representation of the geographical sizes of EU member countries. Using a Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection, the map allows viewers to assess the relative areas of each member state without the distortion often encountered in traditional maps. This exercise highlights how challenging it can be to gauge the size and order of irregularly shaped territories merely by eye.
Deep Dive into EU Member States by Area
Understanding the size of countries within the European Union goes beyond simple numbers; it helps us appreciate the diversity of landscapes, cultures, and economies across the continent. The EU comprises 27 member states, with a collective area of about 4.23 million square kilometers. However, the size distribution among these countries is quite varied.
At the top of the list is France, covering approximately 551,695 square kilometers. What's fascinating is that France's size allows it to host a vast range of geographical features, from the snow-capped peaks of the Alps to the sun-drenched beaches of the French Riviera. In stark contrast, Malta is the smallest member state, with an area of only about 316 square kilometers. This tiny island nation is rich in history and culture, demonstrating that size doesn't necessarily correlate with significance.
Interestingly, Spain and Sweden follow France closely in size, covering roughly 505,990 and 450,295 square kilometers, respectively. These large countries offer unique ecosystems and diverse climates, impacting everything from agriculture to tourism. For instance, Spain's varied climate ranges from Mediterranean in the coastal areas to semi-arid in the interior, which greatly influences its agricultural practices.
On the other end of the scale, many countries like Luxembourg (2,586 km²) and Cyprus (9,251 km²) are significantly smaller. Luxembourg, despite its small size, is one of the wealthiest countries in the EU, showcasing a thriving economy largely based on banking and finance. Cyprus, while geographically larger than Luxembourg, faces its own challenges, including political division and economic recovery following financial crises.
This variation in size reflects not only geographical diversity but also historical and political complexities. Countries like Germany (357,022 km²) and Italy (301,340 km²) play crucial roles in EU politics, economics, and culture, underscoring the importance of understanding their geographical significance.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the geographical areas of EU member states regionally, several trends emerge. For instance, the larger countries in Western Europe are generally more economically developed and have a significant influence on EU policy. France, Germany, and Italy, collectively known as the founding members of the EU, dominate discussions around trade agreements and political stability.
In contrast, the smaller Eastern European countries, such as Estonia (45,227 km²) and Latvia (64,589 km²), while less influential in terms of sheer area, are critical in discussions about EU expansion and regional security. Their relatively small sizes can sometimes lead to underrepresentation in larger EU debates, yet their strategic locations and histories provide unique perspectives that are invaluable in diplomatic discussions.
Northern European nations like Finland (338,455 km²) and Denmark (43,094 km²) demonstrate how geographical area can correlate with environmental policies. Finland, known for its expansive forests and lakes, has a strong commitment to sustainability, while Denmark leads in renewable energy initiatives. Meanwhile, Southern European countries, such as Greece (131,957 km²) and Portugal (92,212 km²), face challenges related to climate change and economic recovery, further emphasizing the importance of geography in shaping national policies.
Significance and Impact
The geographical sizes of EU member states hold significant implications for various facets of life, including economics, politics, and environmental policies. As the EU continues to navigate challenges like climate change, migration, and economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding the size and scale of its member states becomes increasingly important.
For example, larger states often have more resources to invest in infrastructure and public services, while smaller states may rely on collaboration and EU support for development projects. Furthermore, as the EU grapples with its role in a rapidly changing global landscape, the geographical attributes of its member states will continue to influence their political clout and economic strategies.
In conclusion, the map of EU member states by area not only serves as a visualization of size but also opens discussions about the complexities of European unity and diversity. As we move forward, recognizing the significance of each member state's geographical footprint will be vital in shaping the future of the European Union.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 23, 2025
- Views
- 202
Comments
Loading comments...