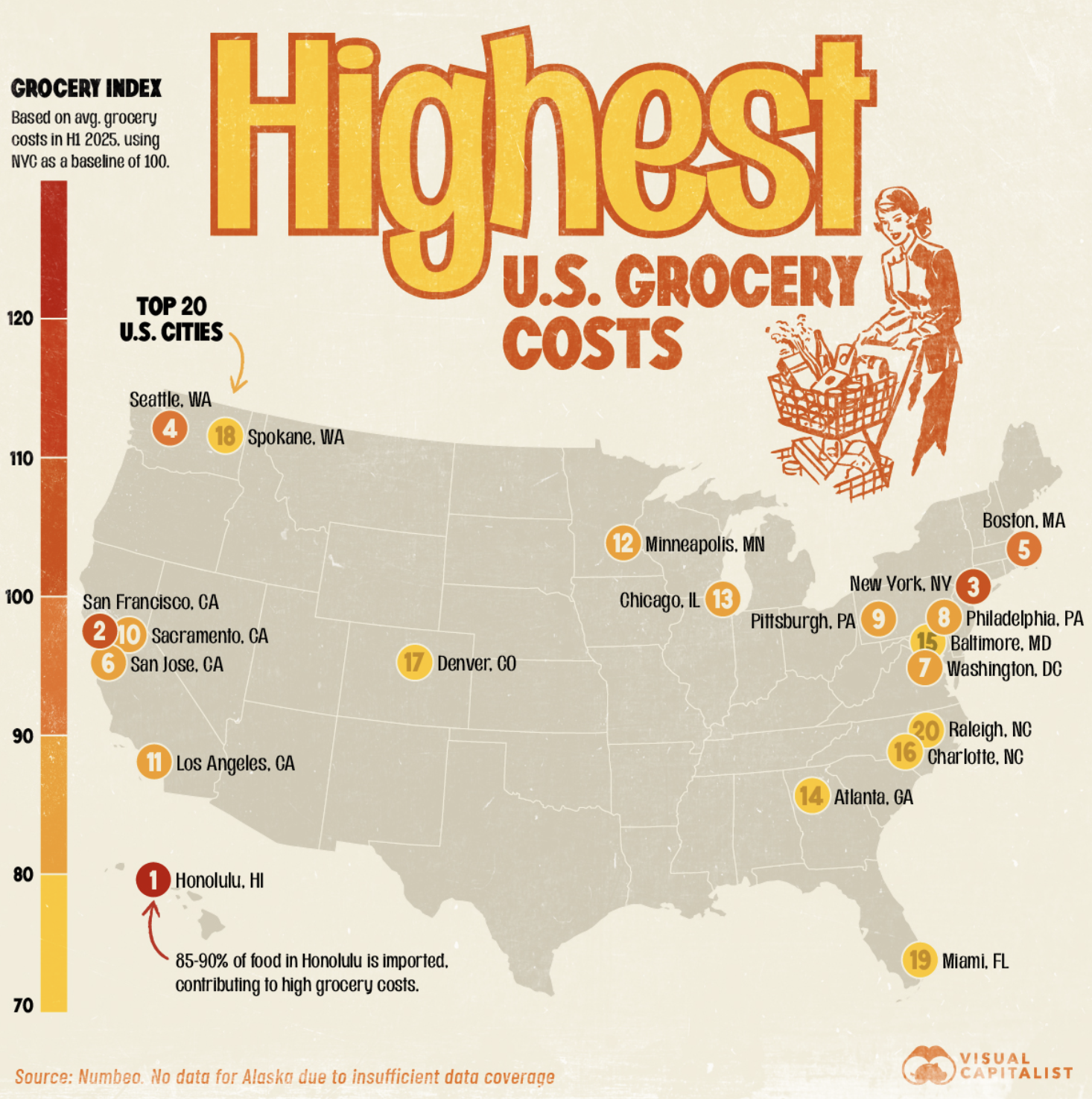
Grocery Cost Map of U.S. Cities

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "MapsRanked: U.S. Cities With the Highest Cost of Groceries" visualization provides a comprehensive snapshot of grocery prices across various cities in the United States. It highlights the disparity in grocery costs, revealing which urban areas are the most expensive for everyday food items. This map serves as a vital tool for residents, prospective movers, and economists alike, illustrating not just where people pay more for groceries, but also hinting at broader economic conditions that may influence these costs.
Deep Dive into Grocery Costs
Grocery costs are influenced by a myriad of factors, including local economies, supply chain logistics, urban density, and even regional agricultural practices. Interestingly, the price of groceries isn't just about the cost of food itself, but also encompasses transportation costs, labor expenses, and market competition.
For instance, cities like New York and San Francisco consistently rank among the highest in grocery prices. In New York, a simple loaf of bread can cost upwards of $4, while fresh produce can be significantly more expensive than in less densely populated areas. This phenomenon can be attributed to high rent, a robust minimum wage, and a competitive marketplace that drives up prices. On the other hand, cities in the Midwest, such as Indianapolis or Omaha, often report lower grocery costs due to lower living expenses and more direct access to agricultural resources.
Moreover, the type of grocery store prevalent in an area can also impact pricing. For example, urban centers are often home to specialty stores and organic markets that cater to specific demographics willing to pay a premium for convenience or quality. In contrast, suburban and rural areas might have more discount grocery chains or larger warehouse stores, which can lead to lower overall grocery prices.
The geographic distribution of grocery costs reveals more than just numbers; it speaks to the economic realities of living in different areas of the U.S. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average American household spends about 10-15% of their income on groceries, but this percentage can be significantly higher in major metropolitan areas.
Interestingly, this disparity can exacerbate existing socioeconomic divides. Families in high-cost areas may find it increasingly difficult to afford nutritious food, leading to issues like food insecurity and reliance on food banks. Additionally, the pandemic highlighted these challenges, as supply chain disruptions caused price spikes in many urban areas.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can identify distinct regional patterns. The Northeast, particularly cities like Boston and Washington D.C., shows a trend of high grocery prices, often exceeding the national average. This is due to a combination of factors such as higher costs of living and elevated demand for fresh, organic produce.
Conversely, the South presents a mixed bag. While cities like Atlanta and Miami have elevated grocery costs, they are often offset by a lower overall cost of living compared to their Northeastern counterparts. In the Midwest, cities like Chicago stand out with their relatively high grocery prices; however, compared to coastal cities, they still remain more affordable.
The West Coast, dominated by cities such as Los Angeles and Seattle, mirrors the high costs seen in the Northeast. Factors such as climate, which allows for year-round produce availability, and a strong economy contribute to these elevated grocery prices. However, the presence of significant agricultural areas nearby, such as California's Central Valley, can sometimes provide more competitive pricing in certain categories.
Significance and Impact
Understanding grocery costs is more than just an exercise in mapping; it has real-world implications for families, policymakers, and businesses. As grocery prices rise in urban areas, the cost of living becomes a critical issue. This can lead to shifts in demographics, as individuals and families seek more affordable living situations, potentially relocating to suburban or rural areas where grocery costs are lower.
Moreover, this data is essential for local governments and organizations aiming to combat food insecurity. By identifying high-cost areas, initiatives can be tailored to provide better access to affordable food options, whether through farmers' markets, community gardens, or food assistance programs.
Looking ahead, trends suggest that grocery costs may continue to rise due to inflationary pressures, supply chain challenges, and changing consumer preferences. As the cost of living increases, it's crucial for both residents and policymakers to stay informed and adapt to these economic shifts, ensuring that access to affordable and nutritious food remains a priority for all.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 18, 2025
- Views
- 124
Comments
Loading comments...