Tribal Population in India Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
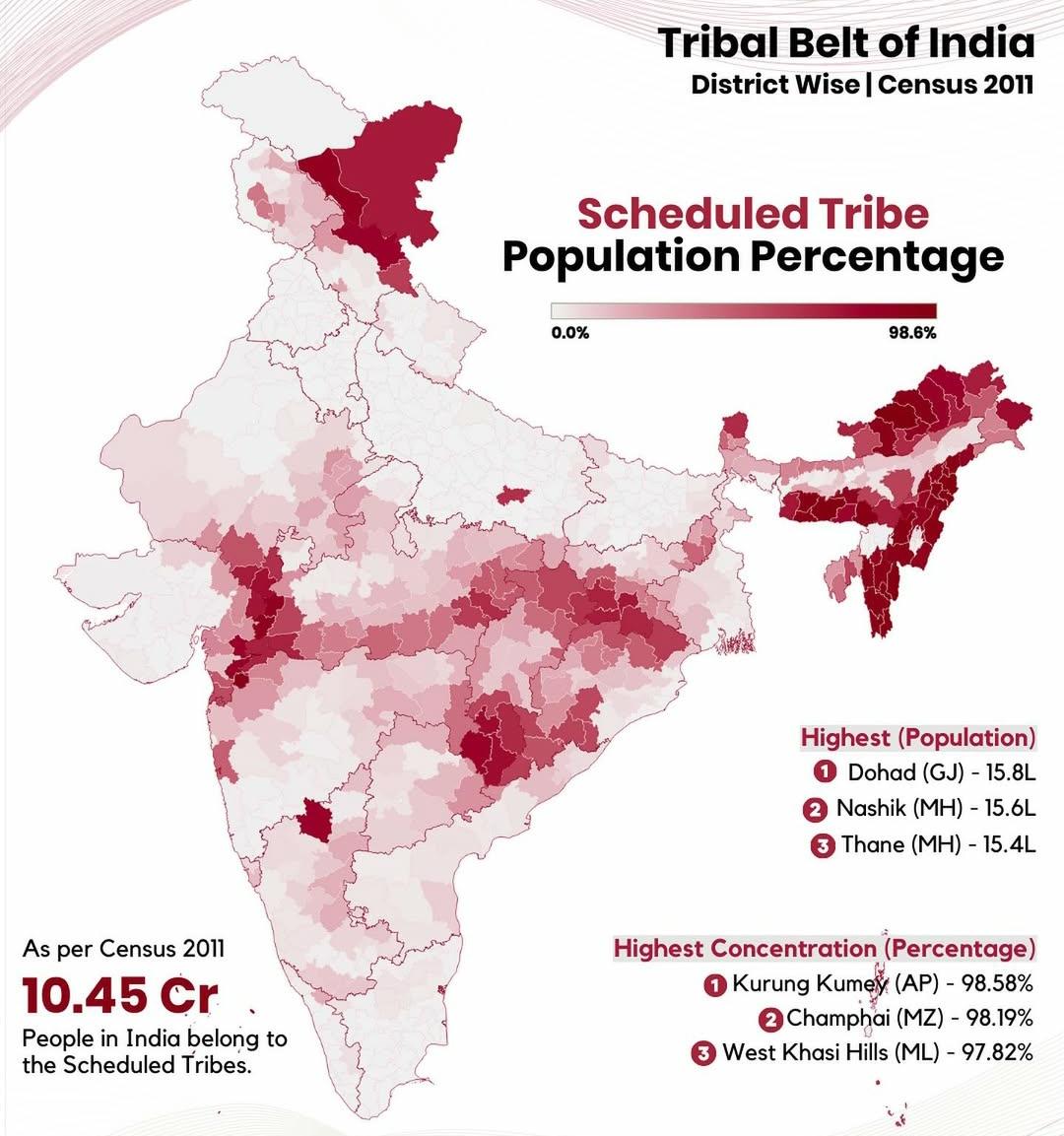
What This Map Shows\nThis map visualizes the distribution of tribal or indigenous populations across India, highlighting regions where these communities are concentrated. Tribal populations in India, often referred to as Adivasis, represent a diverse array of cultures, languages, and traditions. The visualization provides key insights into the demographic makeup of these communities, allowing us to better understand their geographical spread and the factors influencing their population dynamics.
Deep Dive into Tribal Populations in India\nTribal populations in India are incredibly diverse, with over 700 distinct tribes recognized by the Government of India, each with its own unique culture, language, and social structure. According to the 2011 Census, tribal populations constitute around 8.6% of India's total population, amounting to approximately 104 million individuals. This significant number indicates the rich cultural tapestry woven throughout the country.
Interestingly, the tribal population is not evenly distributed across India. The highest concentrations can be found in the central and eastern states, such as Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Jharkhand. These regions are home to significant tribal communities like the Gond, Santhal, and Munda, who have inhabited these areas for centuries. For instance, Madhya Pradesh alone has over 20% of its population belonging to tribal communities, showcasing a profound connection between the land and its indigenous peoples.
However, it’s not just about numbers. The tribal way of life is closely tied to their environment. Many tribes depend on forests for their livelihood, engaging in traditional practices like hunting, gathering, and shifting agriculture. This relationship underscores the importance of sustainable practices, as many tribal communities are facing challenges due to deforestation, land encroachment, and modern agricultural practices that threaten their traditional ways of living.
While some tribal groups are adapting to modernity, others strive to preserve their cultural heritage. For example, the Bhils, one of the largest tribes in India, are known for their vibrant art and music, which are integral to their identity. Unfortunately, many tribes confront socio-economic challenges, including poverty, lack of education, and limited access to healthcare. The government has implemented various policies aimed at improving the living conditions of these communities, but challenges persist.
Regional Analysis\nLooking at the map, several key regions stand out regarding tribal populations. In the northeastern states like Nagaland, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh, tribes like the Naga and the Mizo have distinct cultural identities and languages. The topography of this region, characterized by hills and forests, has allowed these tribes to maintain their traditions while also facing pressures from modernization and migration.
In contrast, in the southern state of Tamil Nadu, the tribes like the Todas and Kotas are facing a declining population due to urban migration and intermarriage. This is a noteworthy example of how urbanization impacts tribal communities differently across regions. Meanwhile, in Gujarat, the Bhil and Warli tribes have been active in advocating for their rights, highlighting the resilience of tribal communities in the face of socio-economic pressures.
Interestingly, the map illustrates that the majority of tribal populations are found in rural areas, pointing to a significant urban-rural divide in India. Many tribal individuals migrate to urban centers in search of employment, leading to a dilution of their cultural practices and languages.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the distribution and dynamics of tribal populations in India is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the need for inclusive policies that respect and preserve the rights of indigenous communities. As India continues to develop economically, it is imperative to ensure that the voices of tribal populations are heard, and their rights are protected.
Moreover, the implications of tribal populations extend beyond cultural preservation. They play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity and environmental sustainability. Many tribal groups are stewards of vast forested areas that are crucial for ecological balance. Recognizing their contributions and integrating their knowledge into conservation efforts can lead to more effective environmental policies.
Looking ahead, ongoing trends indicate that as India becomes increasingly urbanized, the challenges faced by tribal populations will intensify. Addressing issues such as displacement, loss of traditional lands, and cultural assimilation will be essential for protecting the rights and identities of these communities. As we navigate the future, it becomes evident that the preservation of tribal cultures is not just a matter of ethnic identity, but also a vital component of India's rich diversity and heritage.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 16, 2025
- Views
- 114
Comments
Loading comments...