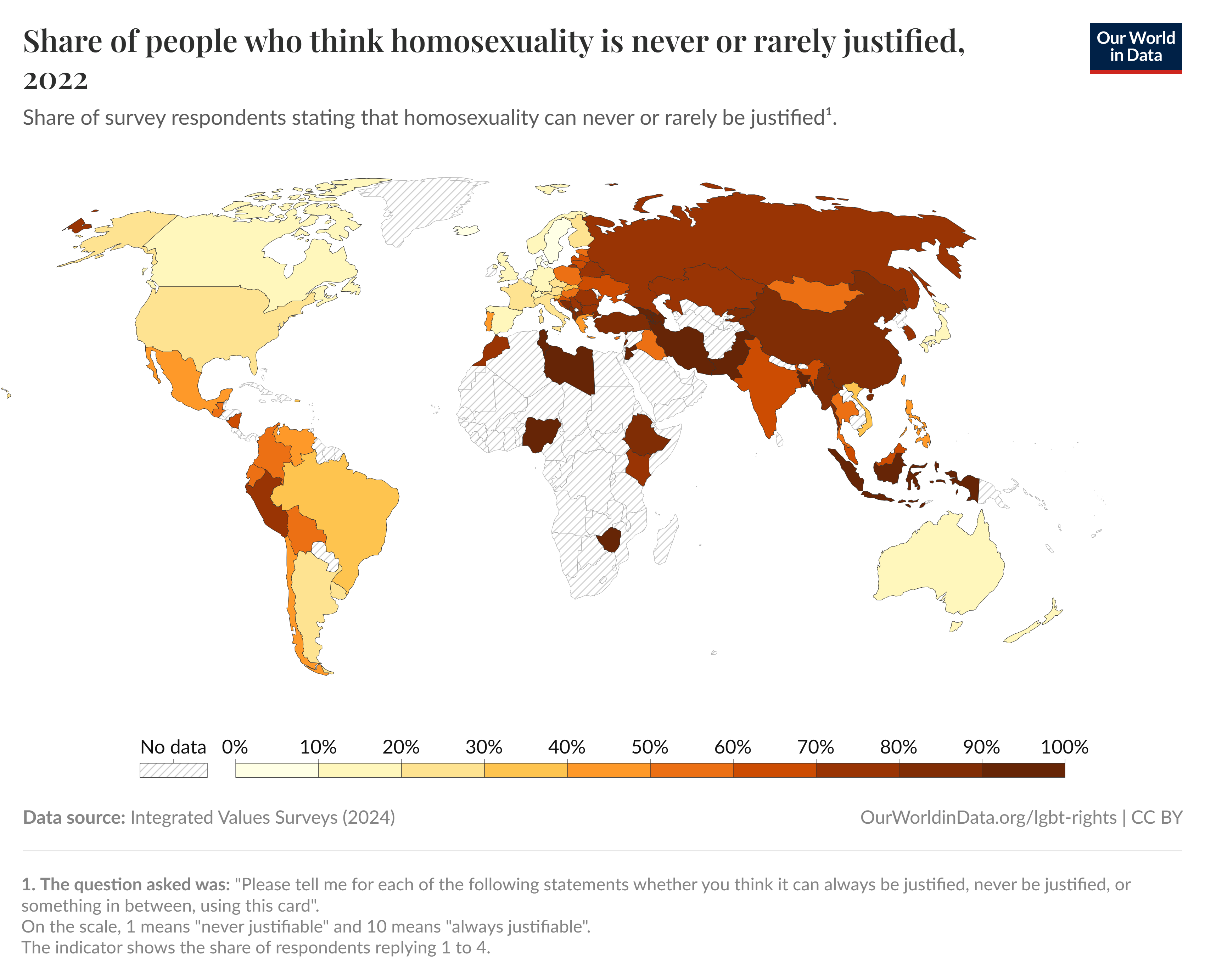
Map of Attitudes Toward Homosexuality, 2022

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Share of people who think homosexuality is never or rarely justified, 2022" provides a visual representation of societal attitudes towards homosexuality across various countries. It highlights the percentage of respondents in each nation who believe that homosexuality is morally unacceptable or rarely justified. Such a visualization serves as a crucial indicator of cultural, religious, and social norms that shape perceptions of LGBTQ+ rights and acceptance around the world.
Deep Dive into Societal Attitudes Toward Homosexuality
Understanding societal attitudes toward homosexuality is essential in grasping the broader context of human rights and social acceptance. The opinions reflected in this map are influenced by various factors, including religion, cultural history, legal frameworks, and social movements. Interestingly, attitudes can span a wide spectrum—from absolute acceptance and legal recognition of same-sex relationships to outright condemnation and criminalization.
In recent decades, many Western nations have made significant strides in LGBTQ+ rights, with countries like Canada, the United States, and several Western European nations embracing same-sex marriage and anti-discrimination laws. In contrast, other regions, particularly in parts of Africa and the Middle East, demonstrate a starkly different attitude, where homosexuality can be met with severe punishment or social ostracism. For instance, in countries like Uganda and Saudi Arabia, a significant percentage of the population views homosexuality as rarely or never justified, reflecting deep-rooted cultural and religious beliefs.
Interestingly, public opinion is not static. Global movements advocating for LGBTQ+ rights have prompted shifts in attitudes, even in traditionally conservative societies. However, these changes can be slow and met with resistance, leading to a complex interplay of acceptance and backlash. For instance, a 2021 survey indicated that while younger generations in some countries are increasingly supportive of LGBTQ+ rights, older generations may hold more traditional views that influence national attitudes.
Furthermore, the stigma associated with homosexuality can lead to significant mental health challenges within LGBTQ+ communities. Studies have shown that in regions where acceptance is low, individuals often face discrimination, leading to higher rates of depression and anxiety. This highlights the importance of fostering inclusive environments where diversity is celebrated rather than condemned.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes apparent that there are notable regional variations in attitudes toward homosexuality. In Western Europe, for example, countries like the Netherlands and Sweden show very high levels of acceptance, with the majority of the population believing that homosexuality is justified. In stark contrast, Eastern Europe presents a mixed picture. While nations like Slovenia show increasing acceptance, countries such as Poland and Hungary reflect more conservative attitudes, often influenced by political rhetoric and religious affiliation.
Moving to Africa, the map reveals a troubling trend. Nations like Nigeria and Uganda demonstrate some of the highest percentages of individuals believing homosexuality is never justified. This is often tied to colonial-era laws that criminalized homosexuality, which remain in effect today, combined with a strong influence of religious conservatism.
In the Americas, attitudes vary widely. While countries like Argentina and Uruguay are known for their progressive stances on LGBTQ+ rights, others, particularly in the Caribbean, show significant resistance. For instance, in Jamaica, a strong anti-LGBTQ+ sentiment persists, making it one of the most challenging environments for sexual minorities.
Significance and Impact
The implications of societal attitudes toward homosexuality extend beyond personal beliefs; they influence legislation, health care access, and overall quality of life for LGBTQ+ individuals. Countries with more accepting attitudes often enjoy stronger protections against discrimination and increased support networks, which can lead to better mental health outcomes for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Moreover, as globalization continues to influence cultural exchanges, the dialogue around LGBTQ+ rights is likely to evolve. The rise of social media has enabled activists to connect across borders, sharing stories and strategies that resonate with people worldwide. This interconnectedness has the potential to challenge oppressive views and promote acceptance, fostering a more inclusive global community.
In conclusion, the map displaying the share of people who think homosexuality is never or rarely justified serves as a critical tool for understanding cultural attitudes toward LGBTQ+ rights. It highlights not only the diversity of opinion across the globe but also the ongoing struggles and triumphs of the LGBTQ+ community. By engaging with these statistics, we can better comprehend the societal changes needed to create a world where everyone, regardless of their sexual orientation, can live freely and authentically.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 12, 2025
- Views
- 142
Comments
Loading comments...