Map of Immigrant Origins in Asia by State

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
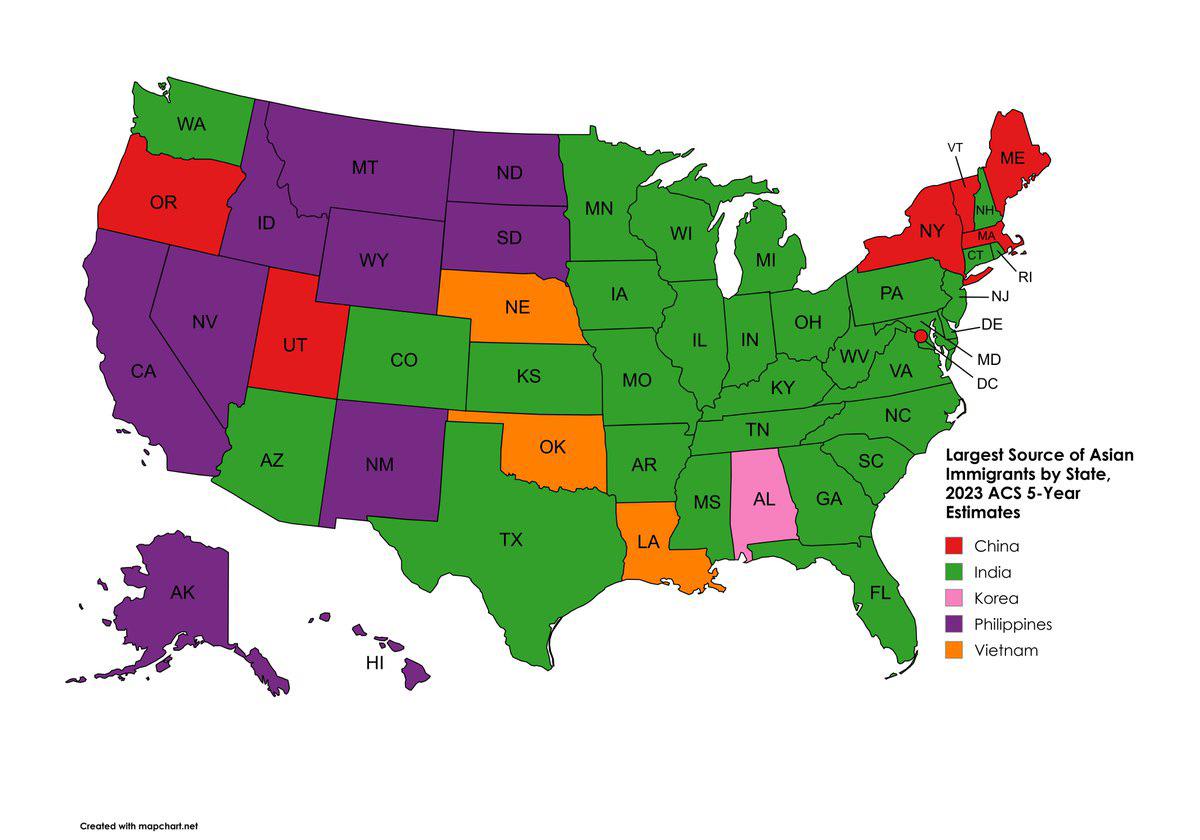
What This Map Shows
The map titled "The Country Where The Most Immigrants in Asia Came From By State" visualizes the origins of immigrants across various states in Asia. Each state is color-coded to represent the primary country of origin for its immigrant population. This geographic visualization provides insight into migration patterns, showcasing how cultural and demographic landscapes vary across the continent.
Immigration has shaped the social and economic fabric of many Asian countries, influencing everything from labor markets to cultural exchanges. As we delve deeper into the topic, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of these migration patterns.
Deep Dive into Immigration Patterns in Asia
Asia is home to some of the world’s largest and most diverse populations, and immigration plays a crucial role in shaping its demographic dynamics. The countries of origin for immigrants in Asia vary greatly, reflecting historical ties, economic opportunities, and regional conflicts.
For example, countries like India and China are notable sources of immigrants due to their large populations and significant diaspora communities. Interestingly, India has consistently ranked as one of the top countries of origin for immigrants in various Asian states. Factors contributing to this include the search for better job opportunities and educational prospects. In contrast, the Philippines is renowned for its overseas workers, with many Filipinos migrating to countries throughout Asia for employment in sectors such as healthcare and domestic work.
Moreover, the Middle East has also emerged as a significant area of origin for immigrants, particularly in Gulf States where labor demand is high. Workers from countries like Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Afghanistan migrate to these regions in search of better economic prospects, contributing to the region's diverse labor force.
What’s fascinating is how these migration trends have led to the emergence of multicultural societies in various Asian states. For instance, Singapore, with its robust economy, has attracted a large number of immigrants from India, China, and Malaysia, creating a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions.
Statistics reveal that nearly one in four people in Singapore is a foreign national, highlighting the country's reliance on immigrant labor. This phenomenon is not isolated; similar trends can be observed in other nations like Malaysia and the United Arab Emirates, where immigrant populations significantly outnumber locals.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can see distinct regional patterns in immigration across Asia. In East Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea show a rising trend in immigration from neighboring nations such as China and Vietnam. However, these nations have traditionally been less open to immigration compared to their Southeast Asian counterparts.
In Southeast Asia, countries like Thailand and Malaysia stand out with significant immigrant populations from Myanmar and Indonesia, respectively. Malaysia, in particular, has a complex demographic makeup, with a substantial number of immigrants from both legal and illegal backgrounds, creating a unique socio-political situation.
Furthermore, the Central Asian states exhibit different trends, where labor migration is often directed towards Russia. Countries like Uzbekistan and Tajikistan have large populations working abroad, primarily in Russia, which has substantial economic ties to the region. This dynamic creates a unique situation where the outflow of people impacts the economic conditions back home.
Significance and Impact
Understanding immigration patterns in Asia is crucial for several reasons. First, these trends have profound implications for economic development. Countries with high immigrant populations often benefit from diverse skill sets, filling labor shortages and contributing to economic growth. However, this also raises questions about integration and social cohesion among local populations and immigrants.
Moreover, the socio-economic impacts of immigration cannot be ignored. For instance, the influx of immigrant workers can lead to both competition for jobs and cultural enrichment, but it can also lead to tensions if not managed properly. This duality is a significant conversation in many Asian nations today, as they grapple with balancing economic needs and social harmony.
Currently, many Asian countries are reassessing their immigration policies in light of changing global dynamics. With the COVID-19 pandemic reshaping labor markets, countries are now reconsidering how to attract skilled workers and address labor shortages in critical sectors. Future projections suggest that immigration will continue to be a vital component of Asia's economic landscape, influencing everything from urban development to cultural exchange.
In conclusion, this map not only reflects the origins of immigrants in Asia but also encapsulates the broader narrative of migration, highlighting the interconnectedness of nations in an increasingly globalized world. As immigration patterns evolve, they will undoubtedly continue to shape the demographic and cultural landscapes of Asia for years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 8, 2025
- Views
- 100
Comments
Loading comments...