Administrative Dioceses of the Roman Empire Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
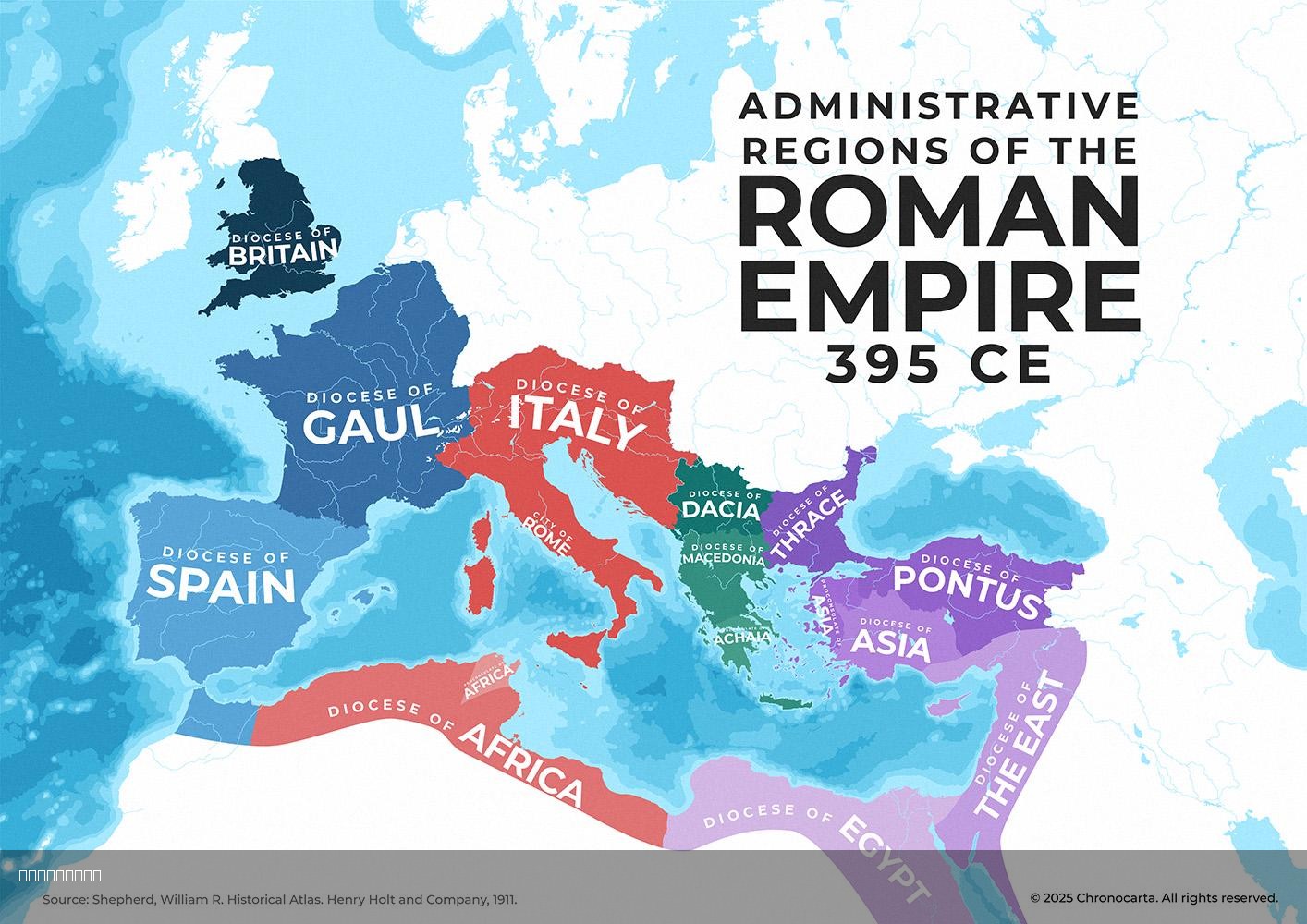
The visualization titled "Administrative Dioceses of the Roman Empire in 395 CE with Proconsular Provinces Highlighted" provides a detailed representation of the administrative divisions of the Roman Empire during a pivotal year in its history. In 395 CE, following the death of Emperor Theodosius I, the empire was permanently divided into Eastern and Western realms. This map highlights the dioceses—regional groupings of provinces overseen by a vicarius—as well as the three significant Proconsular Provinces: Asia, Africa, and Achaia, which reported directly to the emperor. Understanding these divisions is crucial for appreciating the administrative complexity and governance structure of the Roman Empire at its zenith.
Deep Dive into Administrative Dioceses
Dioceses were a fundamental aspect of the administrative framework of the Roman Empire. Each diocese encompassed several provinces, allowing for more efficient governance and coordination of resources, military, and taxation. The vicarius, appointed to oversee the diocese, acted as a crucial intermediary between the emperor and provincial governors. This system was not only practical but also reflective of the empire's vastness, which demanded a sophisticated hierarchy to maintain order across its territories.
What’s fascinating is how these diocesan divisions evolved over time. Initially, the Roman Empire was divided into provinces, but as the empire expanded, it became necessary to create larger administrative units. By the late 4th century, these dioceses had become standard, with each comprising several provinces: for instance, the Diocese of Asia included provinces like Bithynia and Galatia, while the Diocese of Africa contained provinces such as Carthage and Numidia.
The Proconsular Provinces—Asia, Africa, and Achaia—were particularly significant, as they were among the wealthiest and most culturally vibrant areas of the empire. They reported directly to the emperor, bypassing the vicarii, which indicates their importance. For example, the province of Asia was not only an economic powerhouse due to its fertile lands and trade routes but also a cultural hub where Hellenistic influences remained strong, contributing to the rich tapestry of Roman life.
Moreover, the diocesan system facilitated the spread of Christianity as it began to gain followers across the empire. Local bishops often operated within these diocesan structures, and the organization of church authority mirrored civil governance, which helped solidify the church’s influence in the years following Theodosius I's reign.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map by regions reveals the distinct characteristics and administrative challenges each diocese faced. The Eastern dioceses, such as the Diocese of Thrace and the Diocese of Asia, were strategically significant due to their proximity to the borders of the empire. These areas often faced invasions and unrest from barbarian tribes, making strong administrative oversight crucial. For example, the Diocese of Asia, with its bustling cities like Ephesus and Smyrna, was vital for trade and military logistics, leading to a greater need for robust governance.
In contrast, the Western dioceses, such as the Diocese of Gaul and the Diocese of Italy, dealt with different issues. The Western Empire faced increasing internal strife and pressure from Germanic tribes. In these regions, the vicarii had to balance military readiness with governance, often leading to tensions between local needs and imperial directives.
Interestingly, the Proconsular Provinces, while directly overseen by the emperor, also exhibited unique characteristics. For instance, the province of Africa was renowned for its grain production, crucial for feeding the populace of Rome, while Achaia was known for its rich cultural heritage, making it a center for art and philosophy. This diversity within the provinces contributed to the complexity of governance within the dioceses.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the administrative dioceses of the Roman Empire in 395 CE is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. The governance structures established during this period set the foundation for many modern administrative systems. The concept of regional governance, with appointed officials overseeing multiple jurisdictions, can still be seen in contemporary governmental frameworks.
Moreover, as we analyze the legacy of the Roman Empire, it becomes clear that the diocesan model influenced the spread of Christianity and the establishment of ecclesiastical territories that mirror civil divisions. The organizational principles laid out in this era continue to resonate in various political and religious systems today.
In conclusion, the map of the administrative dioceses in 395 CE offers a glimpse into the sophisticated governance of the Roman Empire. It highlights how the empire managed its vast territories and reflects the social, economic, and cultural dynamics of the time. Understanding these historical frameworks allows us to appreciate the complexities of modern governance structures and the enduring influence of Roman administrative practices.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 6, 2025
- Views
- 144
Comments
Loading comments...