Onion Consumption Per Capita in Asia Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
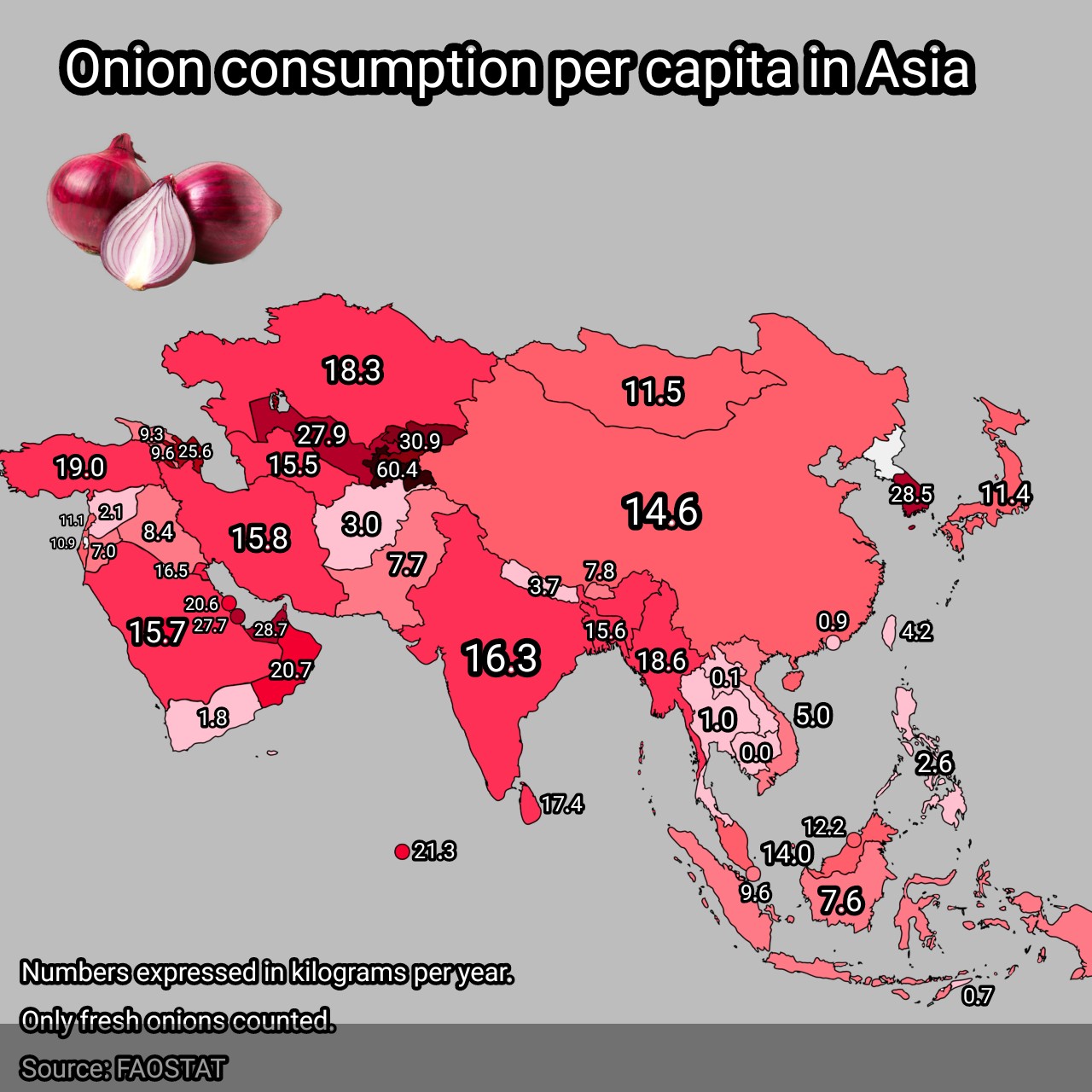
What This Map Shows
The "Onion Consumption Per Capita in Asia Map" provides a visual representation of how much onions are consumed by individuals across various Asian countries. Onion consumption is an interesting metric as it reflects dietary preferences, agricultural practices, and even the economic conditions of nations. This map highlights the disparities in per capita onion consumption, allowing us to delve into cultural significance, agricultural production, and the dietary habits that shape these numbers.
Deep Dive into Onion Consumption
Onions are one of the most widely consumed vegetables globally. They serve as a fundamental ingredient in numerous cuisines, offering flavor and enhancing the nutritional value of dishes. In Asia, onion consumption varies significantly from country to country, influenced by culinary traditions, agricultural output, and local preferences.
Interestingly, India stands out as the largest consumer of onions in Asia, with an impressive per capita consumption rate. The incorporation of onions into everyday cooking, from curries to salads, makes them a staple in Indian households. In fact, onions are so integral to Indian cuisine that they often symbolize prosperity and wealth.
Countries like China and Indonesia also demonstrate high levels of onion consumption, reflecting their diverse culinary practices. In China, onions are used in stir-fries, soups, and as flavor enhancers in various dishes. Meanwhile, in Indonesia, they are a key ingredient in many traditional recipes, including sambals and rich, savory stews.
Contrastingly, Cambodia appears as an outlier on the map. While Cambodians do consume onions, their per capita consumption is significantly lower compared to their regional neighbors. This can be attributed to the country's culinary focus on other ingredients, such as rice, fish, and fresh herbs, which may overshadow the role of onions in daily meals.
The varying rates of onion consumption can also be tied to agricultural production. Countries that produce onions in abundance, like India, are more likely to have higher consumption rates. India is not only one of the largest consumers of onions but also ranks as one of the top producers globally. This local availability makes onions a staple in daily diets. On the other hand, countries with limited agricultural output may have lower consumption rates due to higher prices or reduced availability.
Regional Analysis
When dissecting the map, we can see distinct patterns emerge across Asia. For instance, South Asian countries, such as India and Pakistan, exhibit high levels of onion consumption, often exceeding 10 kg per person annually. This is in stark contrast to countries in Southeast Asia, like Thailand and Cambodia, where consumption rates are noticeably lower, often under 5 kg per person.
In Central Asia, countries like Uzbekistan also show considerable onion consumption, primarily due to traditional dishes that heavily feature onions. Interestingly, in countries like Japan and South Korea, while onions are consumed, they are often used in smaller quantities compared to their South Asian counterparts.
The Middle East, meanwhile, presents a varied picture. Nations such as Iran and Turkey utilize onions extensively in their rich, spiced dishes, contributing to higher per capita consumption rates. The cultural significance of onions in these regions cannot be understated, as they often represent flavor and are essential to traditional cooking methods.
Significance and Impact
Understanding onion consumption in Asia is not just a matter of dietary preferences; it has broader implications for agriculture, trade, and health. Onions are known to have various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory properties and potential cancer-fighting capabilities. Therefore, higher consumption rates can be indicative of healthier dietary practices in certain regions.
Moreover, the global onion market is influenced heavily by the consumption trends in Asia. As countries seek to balance production with consumption, fluctuations in demand can affect market prices and availability. With increasing urbanization and shifts in dietary habits, it will be fascinating to see how onion consumption evolves in the coming years. Will countries like Cambodia increase their intake as they adopt more diverse culinary practices? Only time will tell.
In conclusion, the "Onion Consumption Per Capita in Asia Map" offers valuable insights into not only how much onions are consumed but also the cultural, agricultural, and economic factors that contribute to these patterns. As consumers become more health-conscious and culinary diversity expands, monitoring these trends will be essential for understanding food systems in Asia and beyond.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 6, 2025
- Views
- 174
Comments
Loading comments...