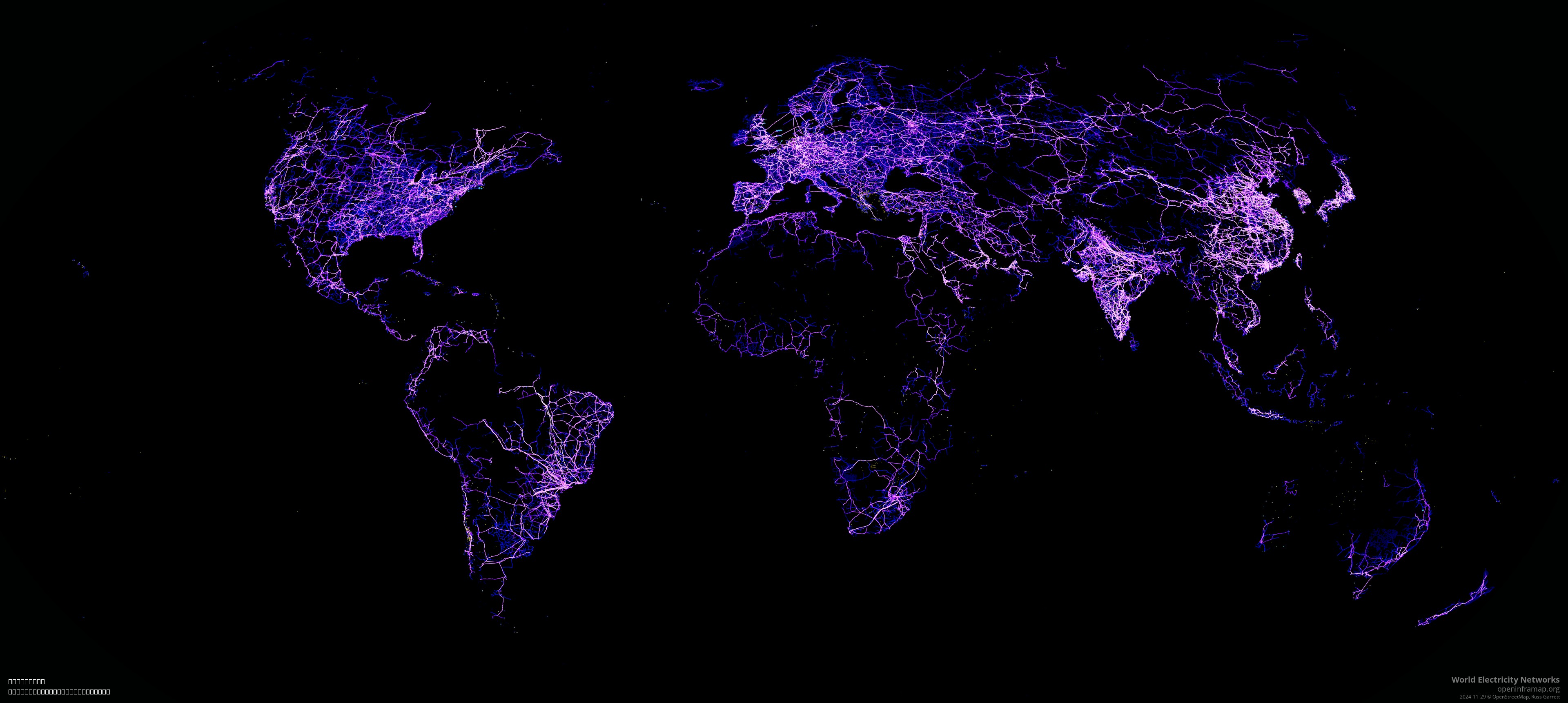
World Electricity Transmission Grid Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows\nThe 'World Electricity Transmission Grid Map' visualizes approximately 70% of the global electrical transmission grid data sourced from OpenStreetMap. This extensive mapping showcases the intricate network of power lines that crisscross countries, connecting generation sites to consumers, thus forming the backbone of national and international electricity supply systems. With this visualization, one can see the vast web of electricity distribution that powers our homes, industries, and cities.
Deep Dive into Global Electricity Transmission\nElectricity transmission is a critical component of our modern infrastructure, facilitating the movement of electrical energy from power plants to substations and ultimately to consumers. The process begins at generation sites, which may utilize diverse energy sources such as fossil fuels, nuclear power, or renewables like wind and solar.
Interestingly, the transmission grid operates at high voltages to reduce energy loss during transit. High-voltage lines can transport electricity over long distances—sometimes hundreds of miles—allowing for efficient access to energy generated in remote areas. For example, many wind farms located in rural regions supply energy to urban centers, demonstrating the importance of a robust transmission network.
The global energy landscape is evolving, especially with the increasing integration of renewable energy sources. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy is expected to account for 80% of the growth in global electricity generation through 2030. This transition necessitates an adaptable and comprehensive electricity transmission grid that can accommodate the variability of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, which are not always available on-demand.
However, the electricity transmission grid also faces significant challenges. Aging infrastructure, regulatory barriers, and geopolitical tensions can impede the development of an efficient and integrated grid. For instance, in the United States, some regions have outdated transmission lines that struggle to keep up with demand, leading to outages and inefficiencies. In contrast, countries in Europe are actively working towards a unified grid to facilitate energy trading and improve resilience against disruptions.
Regional Analysis\nWhen examining the electricity transmission grid across various regions, notable disparities emerge. In North America, the grid is divided into three major interconnections: the Eastern, Western, and Texas Interconnections. Each of these networks operates independently but is interconnected, allowing for some electricity exchange. The Texas grid, for instance, is often discussed for its unique operational independence, which allows it to manage its electricity supply without federal regulation, presenting both opportunities and risks.
In Europe, the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) has been instrumental in fostering cross-border electricity trading. Countries like Germany and France play pivotal roles in this network, exporting excess renewable energy to nearby nations. Conversely, in parts of Africa, the electricity transmission grid remains underdeveloped, with many areas relying on localized power generation. The African Union's Agenda 2063 aims to enhance energy connectivity across the continent, promoting initiatives to create a more integrated and efficient grid.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the global electricity transmission grid is vital for grasping how energy is produced and consumed across different regions. The implications of an efficient transmission grid extend beyond mere electricity supply; they affect economic development, environmental sustainability, and energy security. A well-structured grid can facilitate the smoother integration of renewable energy sources, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
As we move towards a more electrified future, characterized by electric vehicles and smart technologies, the demand for a robust and efficient electricity transmission grid will only increase. The ongoing efforts to complete the mapping of the global electrical transmission grid, aiming for 100% coverage, are crucial in supporting these developments. By participating in initiatives like [Map Your Grid](https://mapyourgrid.org/), individuals can contribute to this essential endeavor, ensuring that our understanding of the electricity transmission network keeps pace with the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 5, 2025
- Views
- 200
Comments
Loading comments...