European Nations Stance on the Iraq War Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
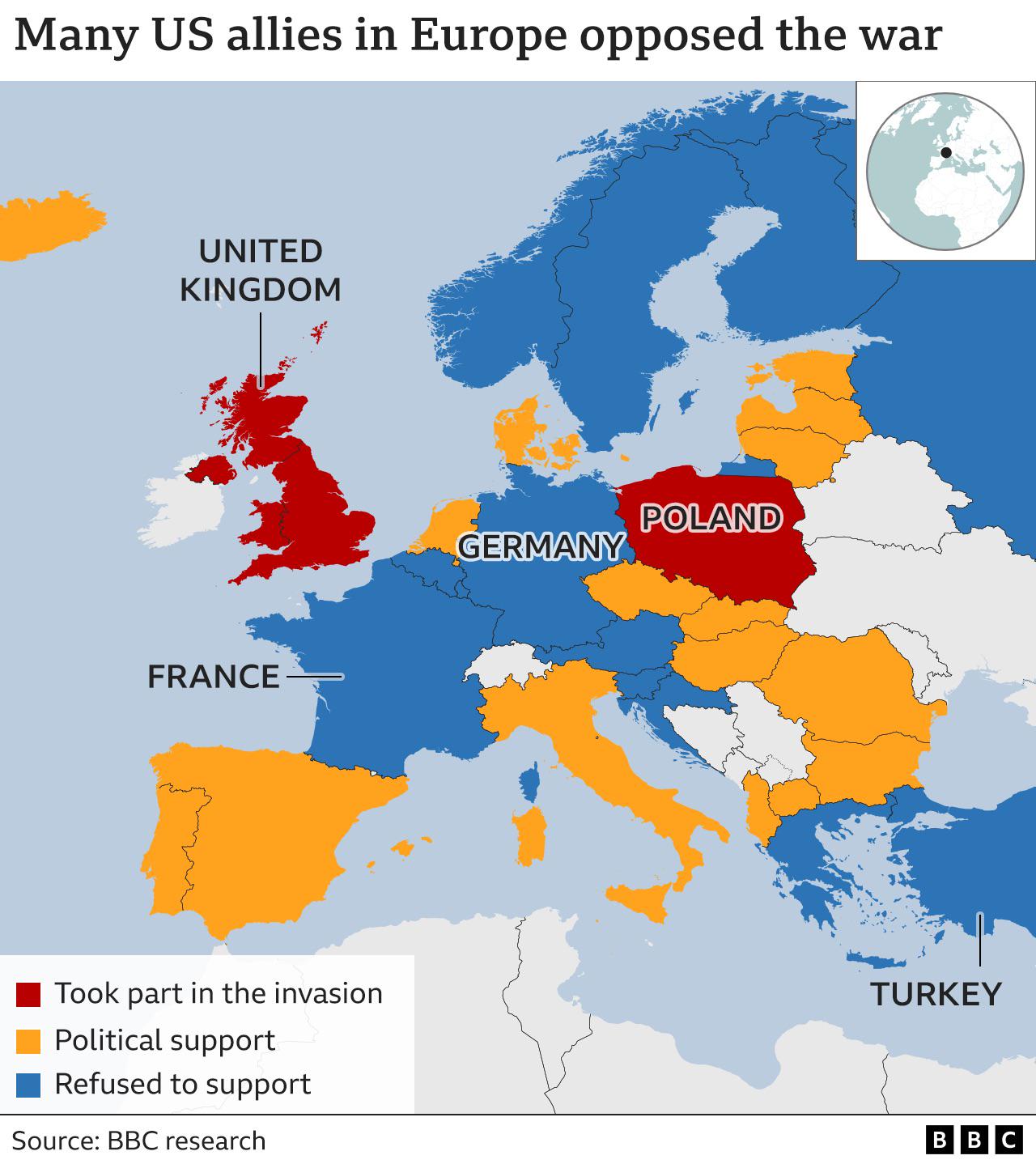
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "European Nations Stance on the Iraq War Map" illustrates the varied positions taken by European countries regarding the involvement in the Iraq War, which began in 2003. This map categorizes nations into distinct groups based on their levels of support or opposition to the military intervention led by the United States. The colors and symbols used in the map provide a clear and immediate understanding of how different nations aligned themselves during this pivotal geopolitical event.
Transitioning into the actual topic, the Iraq War and its implications on European politics and public opinion reveal a complex landscape of alliances, dissent, and the struggle for unity amidst differing national interests.
Deep Dive into the Iraq War and European Response
The Iraq War was a significant military conflict that not only altered the course of Iraq's history but also reshaped international relations, particularly within Europe. It was prompted by the belief that Iraq possessed weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) and posed a threat to global security. However, as the war unfolded, it became increasingly evident that the intelligence regarding WMDs was flawed. This realization led to widespread protests across Europe, reflecting the deep divisions in public sentiment about military intervention.
Interestingly, countries such as the United Kingdom and Spain were among the staunch allies of the United States in this endeavor, demonstrating a commitment to transatlantic relations. On the other hand, nations like France and Germany openly opposed the war, emphasizing a preference for diplomatic solutions and multilateralism through institutions like the United Nations. This divide was not just political but also rooted in historical relationships, national security concerns, and public opinion.
The map categorizes these stances into shades of support, neutrality, and opposition. For example, the UK's decision to send troops highlighted its historical ties to the U.S., while France's resistance reflected a long-standing skepticism towards unilateral military action without UN backing.
Public opinion played a crucial role in shaping these stances. In many European countries, large-scale protests erupted, showcasing a vigorous civil society that opposed the war. For instance, in Germany, Chancellor Gerhard Schröder campaigned on a platform of anti-war sentiment, which resonated with a populace largely against military intervention. This grassroots opposition was a defining feature of the European response, illustrating a unique dynamic where politicians had to navigate between international alliances and domestic public opinion.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map by specific regions, distinct patterns emerge. In Western Europe, the support for the Iraq War varied significantly. The UK, under Tony Blair, played a pivotal role as a U.S. ally, contributing troops and resources. Conversely, countries like Belgium and the Netherlands expressed a more reluctant stance, favoring caution and dialogue over military action.
In Southern Europe, Spain's involvement under Prime Minister José María Aznar was initially supportive; however, the subsequent backlash and electoral defeat in 2004 led to a withdrawal of troops, showcasing how rapidly public sentiment can shift.
Eastern European nations had a more nuanced approach, often motivated by aspirations for closer ties with NATO and the U.S. Many countries in this region, such as Poland and Hungary, supported the invasion in hopes of strengthening their security alliances. However, this support was often met with skepticism from Western European counterparts, highlighting the divergent historical experiences and political contexts within Europe.
Significance and Impact
The stance of European nations on the Iraq War is significant beyond the immediate context of military engagement. It revealed rifts in the European Union and raised questions about the unity and coherence of European foreign policy. The differing positions also set a precedent for future military interventions and the role of international law in legitimizing such actions.
Furthermore, the long-term consequences of the Iraq War continue to resonate today. The rise of extremist groups, the ongoing instability in the region, and the refugee crisis are all interconnected with the decisions made during this period. As we look toward the future, understanding these historical positions aids in interpreting current geopolitical dynamics and the evolving nature of international alliances. Have you noticed how the legacy of the Iraq War still influences debates on interventionism today? The map serves as a poignant reminder of how national interests, public opinion, and historical context shape the geopolitical landscape.
Understanding the stances taken by European nations during this significant conflict provides valuable insights into the complexities of international relations and the importance of collective decision-making in an increasingly multipolar world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 19, 2025
- Views
- 26
Comments
Loading comments...