Electoral College Head of State Appointment Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
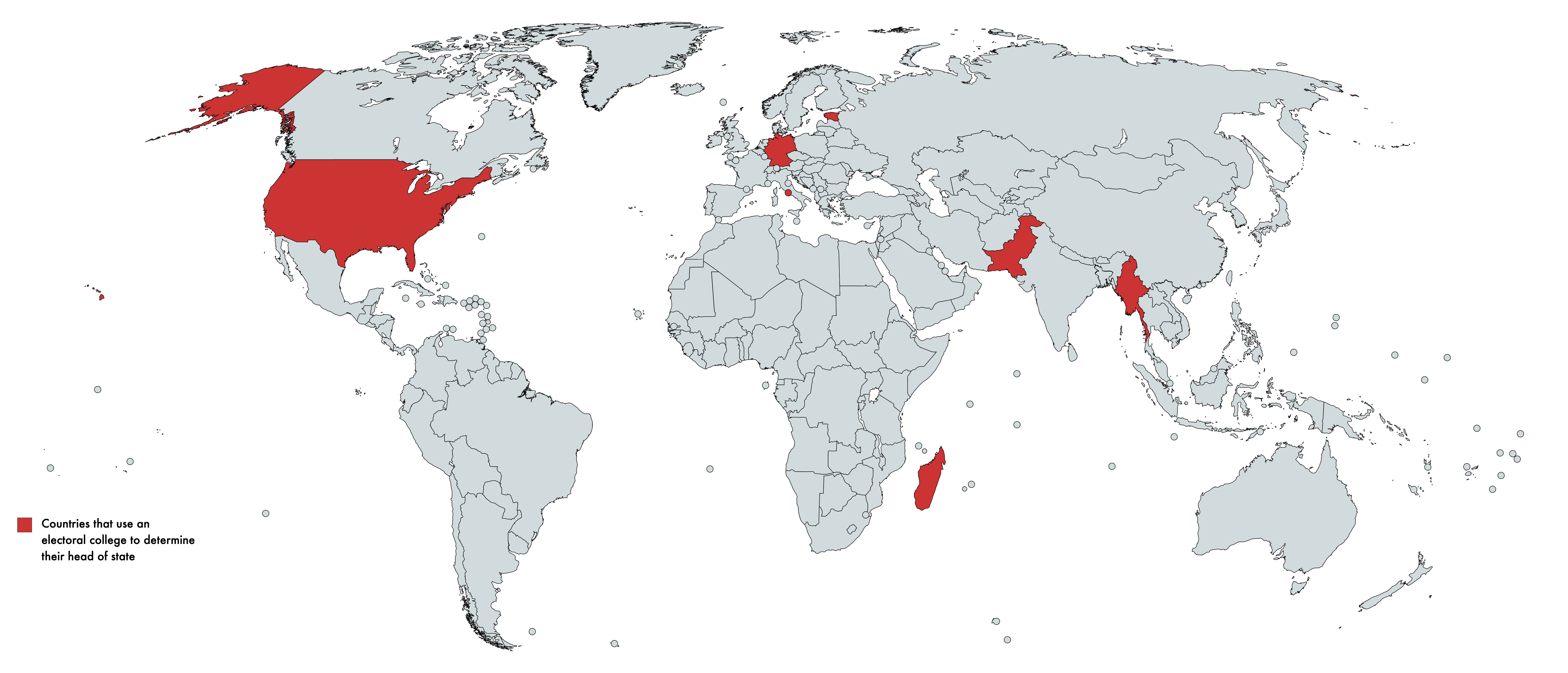
What This Map Shows
This map visually represents the countries around the world that utilize an electoral college system to appoint their head of state. An electoral college is a body of electors established by law, which is typically responsible for formally electing the president or head of state. The countries highlighted on this map show a diverse range of political systems, reflecting varying degrees of democracy, federalism, and representative governance.
While you might be familiar with the concept of electoral colleges in the context of the United States, where the system plays a crucial role in presidential elections, it’s interesting to note that several other nations have adopted similar mechanisms. These systems can vary greatly in their structure and function, influencing not only the electoral process but also the political landscape of the countries involved.
Deep Dive into Electoral College Systems
Electoral colleges serve as a middle ground between direct democracy and representative governance. Instead of citizens directly voting for their head of state, they cast their votes for a group of electors pledged to vote for specific candidates. This system aims to balance the influence of populous regions with less populated areas, attempting to ensure that all voices are considered in the electoral process.
One of the most significant examples of an electoral college system is found in the United States. Here, each state has a certain number of electors based on its population, with a total of 538 electors. To win the presidency, a candidate must secure a majority of these electoral votes. This has led to instances where a candidate can win the presidency without winning the popular vote. Interestingly, this aspect has sparked ongoing debates about the fairness and effectiveness of the system.
Other countries employing electoral college systems include India, which uses a complex system to elect its president through an electoral college composed of the elected members of both houses of Parliament and the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of the States and Union territories. This method reflects India's commitment to federalism and the representation of its diverse population.
In contrast, countries like Brazil and Germany have their own unique systems for appointing their leaders. Brazil utilizes an indirect election for the presidency, where members of the National Congress act as electors. Meanwhile, Germany has a Federal Assembly that elects the Federal President, comprising federal parliament members and representatives from the states.
The variations in these systems illustrate how cultural, historical, and political factors shape electoral processes. In nations with federal structures, electoral colleges can help maintain a balance between local and national interests, ensuring that less populous regions are not overshadowed by major urban centers.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, we can identify several regions where electoral colleges are prevalent. In North America, the United States stands out with its well-known electoral college system. However, Canada operates as a parliamentary democracy without a formal electoral college, using a different mechanism for appointing its prime minister.
In Europe, countries like Germany and Switzerland demonstrate the electoral college model through their unique systems. Germany's Federal Assembly adds a layer of representation that reflects its federal structure, while Switzerland employs a system known as the Federal Council. This council, made up of seven members, acts collectively as the head of state, with each member representing different political parties.
Moving to Asia, India’s electoral college is a fascinating example of how a diverse nation can manage its electoral process. The inclusion of state assembly members as electors ensures that various regional voices contribute to the national decision-making. Conversely, countries like Japan utilize a parliamentary system where the prime minister is not directly elected by the populace but is instead chosen by the legislature.
In Africa, countries like Ethiopia and Nigeria have adopted electoral college systems as part of their federal structures, striving to balance representation among diverse ethnic and regional groups. This approach is particularly important in regions where ethnic tensions can complicate governance.
Significance and Impact
The electoral college systems in various countries have profound implications for governance and democracy. These systems can reflect the values of federalism, aiming to ensure that all regions are represented and that the political power is not concentrated solely in urban centers. However, they also raise questions about the efficacy and fairness of the electoral process.
As we move toward the future, the debate surrounding electoral colleges continues to evolve. With increasing global discussions on electoral reform and the push for more direct forms of democracy, it is essential to consider the role that these systems play in shaping political landscapes. Their influence on voter engagement, representation, and the overall health of a democracy cannot be understated.
Interestingly, as nations grapple with changing demographics and political ideologies, the future of electoral college systems might witness substantial transformations. Will countries choose to maintain these systems, or will they shift toward more direct forms of governance? Only time will tell, but the conversation surrounding electoral representation is more relevant now than ever.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 10, 2025
- Views
- 52
Comments
Loading comments...