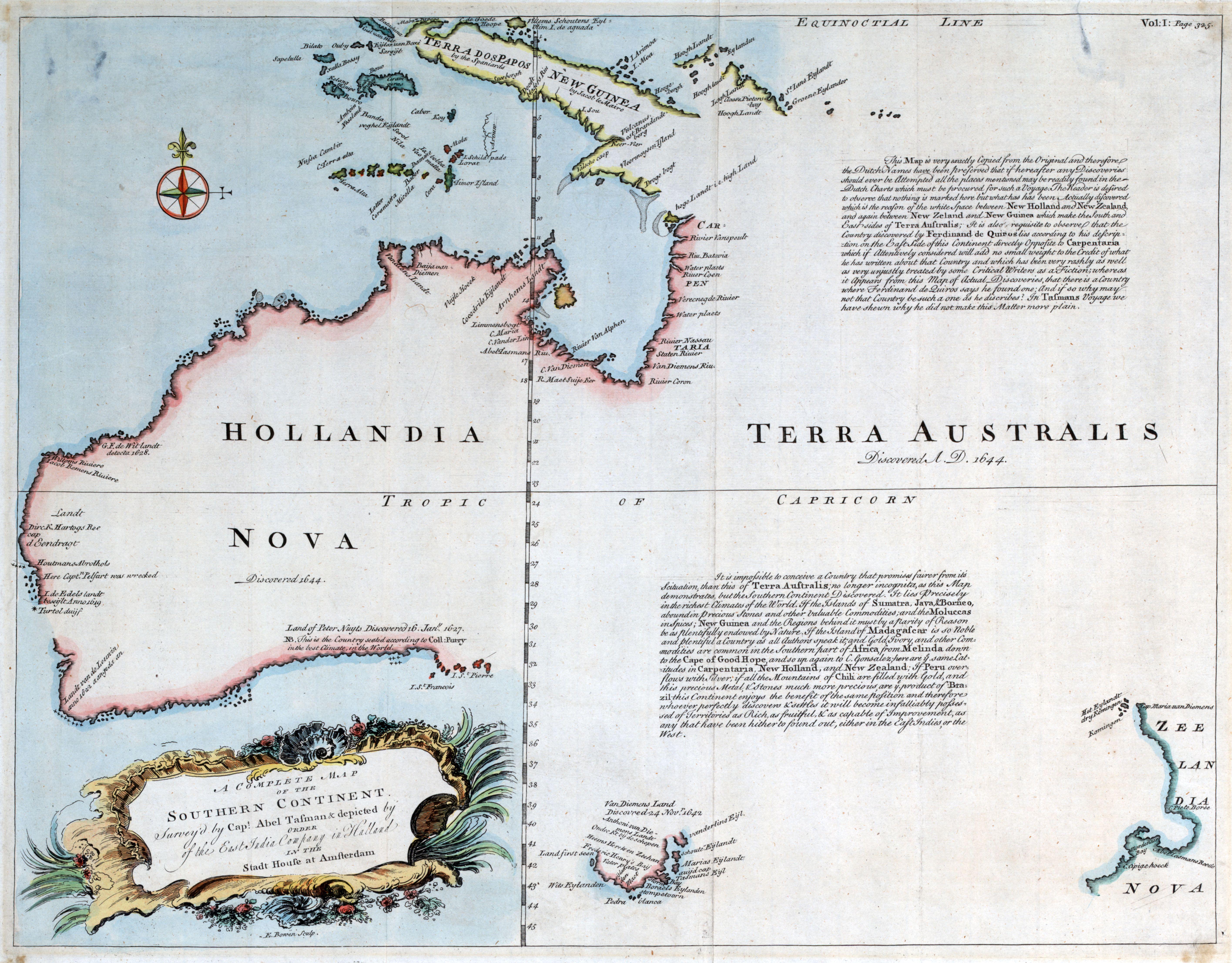
Hollandia Nova Map of Dutch Colonial Settlements

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The Hollandia Nova map provides a detailed visualization of the Dutch colonial settlements established in the Americas during the 17th century, particularly in what is now known as parts of the Caribbean and South America. This map highlights key locations of settlements, trade routes, and areas of military significance, offering a glimpse into the historical footprint of Dutch colonialism.
The Dutch Republic, during its Golden Age, was a formidable maritime power, and its ventures into the Americas were significant not just for the Dutch but for the global trade dynamics of the time. Ever wondered why the Netherlands had such a prominent role in colonization? It’s fascinating to see how a relatively small country managed to establish a vast overseas empire that influenced trade, culture, and politics.
Deep Dive into Dutch Colonial Settlements
Dutch colonialism in the Americas can be traced back to the early 1600s when the Dutch West India Company was established in 1621. This company played a pivotal role in the colonization process, focusing on trade in sugar, tobacco, and slaves. The settlements depicted in the Hollandia Nova map include notable locations such as New Amsterdam (now New York City), the Caribbean islands like Aruba and Curacao, and parts of present-day Brazil.
One of the most interesting aspects of these settlements is their strategic locations. For instance, New Amsterdam was positioned at the mouth of the Hudson River, which offered a prime spot for trade and access to the interior of North America. The Dutch recognized the potential for lucrative trade in furs and other goods, leading to rapid urban development in the area. By the mid-17th century, New Amsterdam had become a bustling hub of commerce, with a diverse population that included Dutch settlers, Africans, and Indigenous peoples.
Interestingly, the Dutch also established a significant presence in Brazil, particularly in the Northeast region, where they controlled large sugar plantations. The map illustrates the critical towns and trade routes that facilitated the Dutch sugar trade, which became a cornerstone of their colonial economy. The interactions between the Dutch settlers and the local Indigenous populations were complex, often marked by both cooperation and conflict, as the Dutch sought to expand their influence.
Moreover, the map reflects the environmental adaptations made by the Dutch in their settlements. The construction of dikes and canals in areas like New Amsterdam mirrored the techniques used in the Netherlands to manage water levels, showcasing the Dutch expertise in hydraulic engineering. This ingenuity allowed them to thrive in an unknown landscape and set the stage for future urban planning in the region.
Regional Analysis
Examining the Hollandia Nova map reveals distinct regional characteristics across the Dutch settlements. In the Caribbean, islands like Curacao and Aruba were primarily utilized as trade posts for the slave trade and sugar production. Their geographic proximity to the mainland made them ideal for the transatlantic slave trade, which fueled the economic engines of the Dutch colonies.
In contrast, the settlements in North America, particularly New Amsterdam, evolved into urban centers that served as melting pots of culture and commerce. The population dynamics were quite different; while Caribbean islands were often sparsely populated with a focus on plantation economies, New Amsterdam attracted a diverse array of settlers. By 1664, when the English seized control, New Amsterdam had become one of the most cosmopolitan cities in North America, reflecting the Dutch legacy of tolerance and trade.
Moreover, the map enables us to understand the competition between European powers in the New World. The strategic placement of Dutch settlements often led to conflicts with the English and the Portuguese, particularly over control of trade routes and resources. The shifting boundaries and allegiances illustrated in the Hollandia Nova map are a testament to the dynamic geopolitical landscape of the 17th century.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the significance of the Hollandia Nova map extends beyond mere historical interest; it sheds light on the long-lasting impacts of colonialism in the Americas. The Dutch influence can still be felt today, particularly in the cultural and architectural heritage of cities like New York. The legacy of trade, urbanization, and cultural exchange initiated by the Dutch has shaped the social and economic fabric of the region.
Moreover, the map serves as a reminder of the complexities of colonial interactions, including the often-overlooked narratives of Indigenous peoples and enslaved Africans who were integral to the colonial economy. As we continue to grapple with the implications of colonial histories in contemporary society, the Hollandia Nova map stands as a vital resource for understanding the past and its enduring influence on current geopolitical realities.
In conclusion, the Hollandia Nova map is more than just a historical artifact; it encapsulates a significant chapter in the story of globalization, trade, and cultural exchange. As we explore its intricacies, we not only learn about the Dutch colonial ventures but also about the interconnectedness of our world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 27, 2025
- Views
- 38
Comments
Loading comments...