Unemployment Rate in the EU July 2025 Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
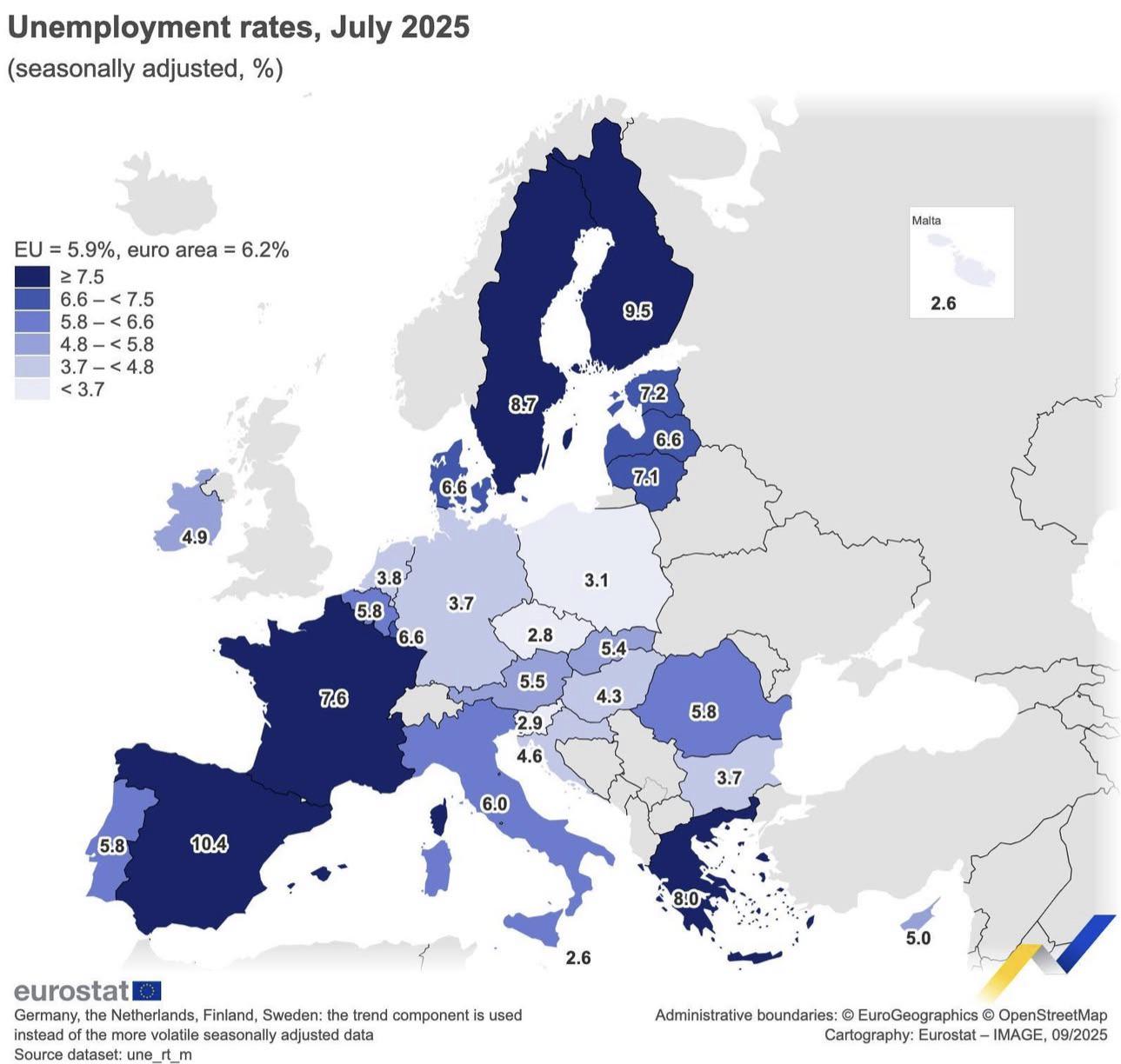
The "Unemployment Rate in the EU July 2025 Map" provides a detailed snapshot of the labor market situation across the European Union at a specific point in time. This visualization highlights the percentage of the workforce that is unemployed in each EU member state, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the disparities and trends affecting employment across the continent.
However, examining unemployment rates is more than just numbers; it tells a compelling story about economic health, social stability, and the resilience of various nations. As we transition into a deeper understanding of unemployment, it’s pivotal to explore the factors that contribute to these rates and what they signify for the people living in these regions.
Deep Dive into Unemployment in the EU
Unemployment is a critical indicator of economic performance, reflecting the ability of an economy to create jobs and sustain livelihoods. In July 2025, the EU faced a complex landscape shaped by various factors, including economic policies, global market dynamics, and post-pandemic recovery efforts. Interestingly, the overall unemployment rate can vary widely from country to country within the EU, influenced by local economic conditions, labor market regulations, and demographic factors.
According to Eurostat data, the EU-wide unemployment rate in July 2025 was approximately 6.8%. However, this figure masks significant disparities. For instance, countries like Germany and the Netherlands boasted rates below 4%, indicating robust job markets and high employment levels. In contrast, southern European nations such as Greece and Spain experienced rates exceeding 12%, reflecting ongoing structural challenges and economic recovery hurdles.
One critical factor affecting unemployment is youth unemployment, which tends to be higher than the overall rate. In July 2025, the average youth unemployment rate in the EU was around 14.5%, with countries like Italy and Spain facing rates above 30%. This demographic often struggles to find stable employment due to a lack of experience and the impact of economic downturns on entry-level jobs.
Moreover, sector-specific trends also play a crucial role in shaping unemployment rates. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated changes in certain industries, leading to job losses in sectors like hospitality and travel, while technology and green energy sectors have seen growth. What's fascinating is how economies are adapting to these shifts, creating new opportunities even as traditional sectors face challenges.
Regional Analysis
Diving deeper into regional differences reveals the nuanced landscape of unemployment across the EU. Northern and Western Europe generally enjoy lower unemployment rates, with countries like Denmark (3.4%) and the Netherlands (3.3%) demonstrating strong labor markets bolstered by diverse economies and proactive labor policies. These nations often emphasize vocational training and education, leading to a more adaptable workforce.
In contrast, the Mediterranean region struggles with higher unemployment. For example, Spain's unemployment rate stood at 13.2%, a stark reminder of the challenges that linger from the financial crises of the past. Similarly, Greece, with an unemployment rate of 14.5%, faces long-term economic restructuring and social implications stemming from its austerity measures.
Eastern European countries, such as Poland and Hungary, typically report rates around the EU average, but they are experiencing rapid changes. Poland, for instance, has seen a significant drop in unemployment over the past decade, aided by a booming labor market and increasing foreign investment. However, challenges remain, particularly in rural areas where job opportunities are limited.
Significance and Impact
Understanding unemployment rates is essential not only for policymakers but also for citizens, as it directly impacts social welfare, economic stability, and community well-being. High unemployment can lead to increased social tensions, higher crime rates, and decreased consumer spending, creating a vicious cycle of economic decline.
Currently, as the EU navigates post-pandemic recovery and grapples with inflationary pressures, monitoring unemployment trends will be crucial in shaping future economic policies. Governments may implement measures to stimulate job creation, enhance vocational training, and support industries most affected by economic shifts.
Looking ahead, it’s vital to consider how automation and digital transformation will influence job markets across the EU. As sectors evolve, the focus on reskilling and upskilling the workforce will become increasingly important to mitigate the effects of unemployment. In this way, the unemployment rate is not just a statistic but a reflection of societal resilience and adaptability in the face of changing economic landscapes.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...