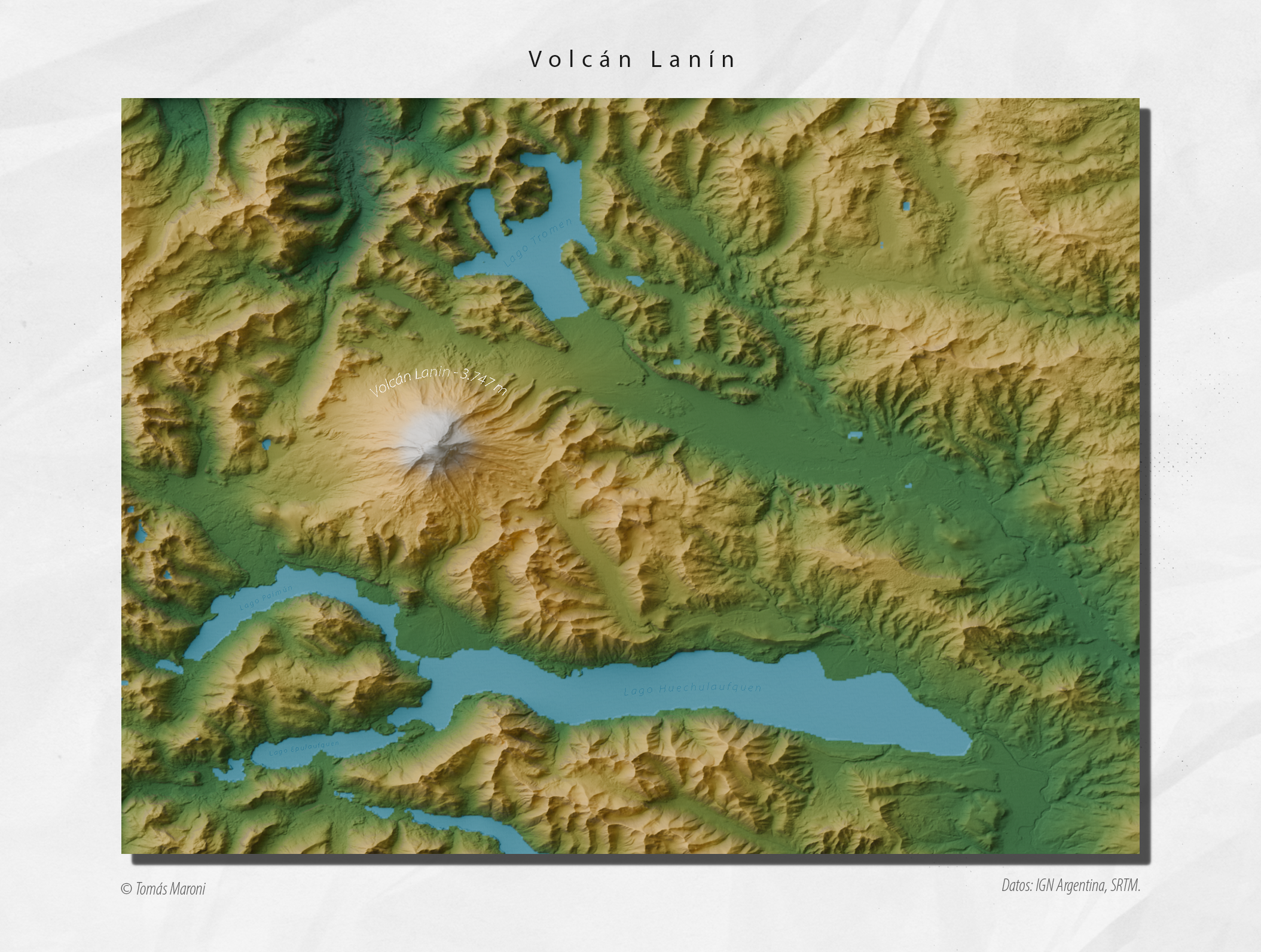
Volcán Lanín Map of Neuquén, Argentina

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Volcán Lanín Map of Neuquén, Argentina" provides a detailed geographical representation of Volcán Lanín, a prominent stratovolcano located within the Andes mountain range. This visualization not only marks the location of the volcano but also highlights surrounding geographical features such as lakes, rivers, and national parks. Nestled in the Neuquén Province, Lanín is a key landmark that attracts both geologists and outdoor enthusiasts. The map serves as an excellent resource for understanding the volcanic landscape and its natural surroundings.
Deep Dive into Volcanic Activity
Volcán Lanín stands at an impressive height of 3,776 meters (12,389 feet) and is classified as a stratovolcano, characterized by its steep profile and layered structure formed by alternating eruptions of lava and pyroclastic flows. The last known eruption of Lanín occurred in the 20th century, specifically in 1909; however, this volcano remains active in geological terms. Interestingly, the volcanic activity in this region can be attributed to the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate, a process that creates intense geological pressure and leads to volcanic formations.
What’s fascinating is that Lanín is not just a single volcano but part of a broader volcanic arc that includes several other significant peaks in the Andes. The surrounding area is rich in geological history, showcasing various types of volcanic rock and formations. For those interested in geology, the Lanín region offers a unique opportunity to study volcanic processes and their impacts on the landscape.
Additionally, the Lanín National Park, where the volcano is located, is home to diverse ecosystems. The park spans over 1,400 square kilometers and contains a variety of habitats, including forests, lakes, and mountain ranges. The biodiversity in this region is remarkable, with species of flora and fauna that are endemic to the area. The interplay between volcanic activity and ecological systems creates a dynamic environment that continues to evolve.
Regional Analysis
The map allows us to analyze the geographical context of Volcán Lanín in relation to nearby features. To the west lies Lake Lácar, a glacial lake that adds to the scenic beauty of the region. This lake is not only a popular destination for tourists but also plays a crucial role in the local hydrology. The presence of lakes and rivers nearby, such as the Chimehuin River, showcases how volcanic activity has shaped the landscape over millennia.
When comparing the volcanic features of Lanín with other nearby volcanoes, such as Volcán Copahue to the south, we observe distinct differences in eruption history and geographical formation. Copahue, for example, is known for its frequent eruptions and the presence of geothermal activity, including hot springs. In contrast, Lanín's last eruption was over a century ago, making it a more stable feature in the region's geological profile.
Moreover, the cultural significance of Volcán Lanín cannot be understated. The indigenous Mapuche people hold this volcano in high regard, weaving it into their mythology and cultural practices. Understanding the interplay between geography and culture adds another layer to the significance of this landmark.
Significance and Impact
The significance of Volcán Lanín extends beyond its geological features; it also impacts local communities and ecosystems. The volcano and its surrounding national park are vital for tourism, attracting hikers, climbers, and nature lovers. This influx of visitors contributes to the local economy but also raises questions about environmental sustainability.
Current trends show a growing interest in ecotourism in the region, emphasizing the need to balance economic benefits with conservation efforts. As climate change continues to affect weather patterns and ecosystems, the area around Volcán Lanín may experience shifts in biodiversity and water availability. Future projections suggest that monitoring volcanic activity and its environmental impacts will be crucial for both the local populace and visitors alike.
In conclusion, the map of Volcán Lanín not only highlights a geological wonder but also serves as a starting point for discussions about the interplay of natural forces and human impact. The enduring majesty of Lanín symbolizes the dynamic nature of our planet and the importance of preserving these unique landscapes for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 11, 2025
- Views
- 122
Comments
Loading comments...