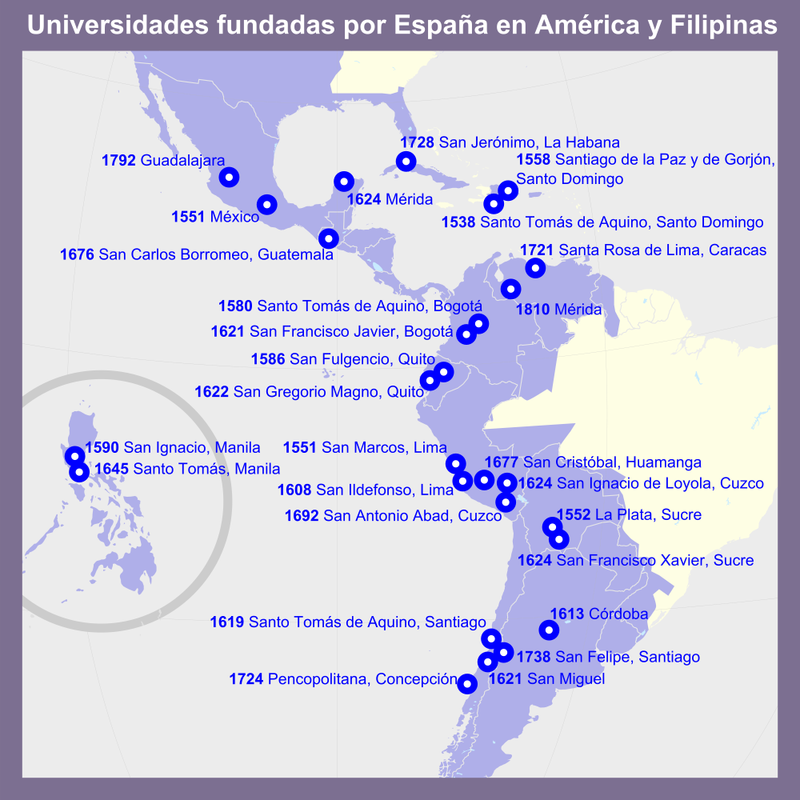
Map of Universities Founded by the Spanish Empire

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the geographical distribution of universities that were established during the period of the Spanish Empire, showcasing a total of 32 institutions across Latin America. It highlights the significant role that the Spanish colonial influence played in shaping higher education in the Americas from the 16th to the early 19th century. However, it's important to note that five universities, such as the Universidad de Managua founded in 1812, are missing from this visualization. This oversight emphasizes the complexity of mapping historical data, as some institutions may not be as widely recognized or documented.
Deep Dive into Universities Founded by the Spanish Empire
The establishment of universities by the Spanish Empire marked a pivotal moment in the educational landscape of Latin America. The first university, the Universidad de Santo Domingo, was founded in 1538 in what is now the Dominican Republic. This institution laid the groundwork for higher education throughout the region, promoting not only academic scholarship but also the spread of European culture and the Spanish language.
Interestingly, the Spanish Empire utilized these universities as tools for assimilating indigenous populations and promoting Catholic doctrine. The curriculum often included theology, law, medicine, and the arts, reflecting the values and priorities of the empire. For example, the Universidad de México, founded in 1551, became a center of intellectual activity, producing influential figures such as Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, a prominent writer and early feminist thinker.
The universities served as hubs for social and political discourse, influencing the development of national identities in the colonies. By the 19th century, as independence movements gained momentum, many of these institutions played crucial roles in shaping the ideologies of emerging nations. The Universidad de Buenos Aires, established in 1821, became a symbol of progressive thought and academic freedom during a time when traditional colonial power structures were being challenged.
Additionally, the spread of these institutions led to significant demographic shifts. They attracted students from various regions, contributing to urbanization and the growth of cities. The presence of a university often catalyzed the development of surrounding communities, resulting in better infrastructure and increased economic opportunities. In this way, the legacy of these universities extends beyond mere education; they have influenced social mobility and economic growth throughout Latin America.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see distinct patterns in the establishment of universities across various regions. For instance, Mexico and Peru were particularly prominent in the founding of educational institutions, with several universities established in urban centers. The Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and the Universidad de San Marcos in Lima are prime examples of how these institutions became central to intellectual life.
In contrast, areas such as Central America and the Caribbean show fewer universities, reflecting the different colonial policies and levels of investment in education. The Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, founded in 1676, highlights the historical significance of education in Central America, but the overall number of institutions remains lower compared to larger territories like Mexico and Peru.
What's fascinating is that while many universities initially focused on European studies, they gradually evolved to incorporate local culture and knowledge systems, particularly in the 20th century. This evolution is evident in universities such as the Universidad de Chile, which has become a leader in social sciences and indigenous studies, signaling a shift toward a more inclusive and representative educational framework.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the legacy of universities founded by the Spanish Empire is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, these institutions laid the foundational structure for higher education in Latin America, influencing educational standards and accessibility. Today, many of these universities continue to be prestigious institutions, shaping the future of education in their respective countries.
Moreover, as we assess the current educational landscape, we can observe ongoing challenges such as equity in access to education and the need for curriculum reforms to better reflect diverse histories and cultures. The historical context provided by the map highlights how colonial legacies still resonate in contemporary society, impacting educational policy and public perception.
Looking forward, the role of these universities will continue to evolve. The push for modernization, integration of technology, and a focus on global citizenship will redefine how these institutions operate in the 21st century. As we examine the future of education in Latin America, the historical foundations laid by the Spanish Empire remain a significant point of reference, reminding us of the intricate tapestry of cultural and intellectual exchange that has shaped the region.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 9, 2025
- Views
- 94
Comments
Loading comments...