Nuclear Triad, Dyad, and Monad Nations Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
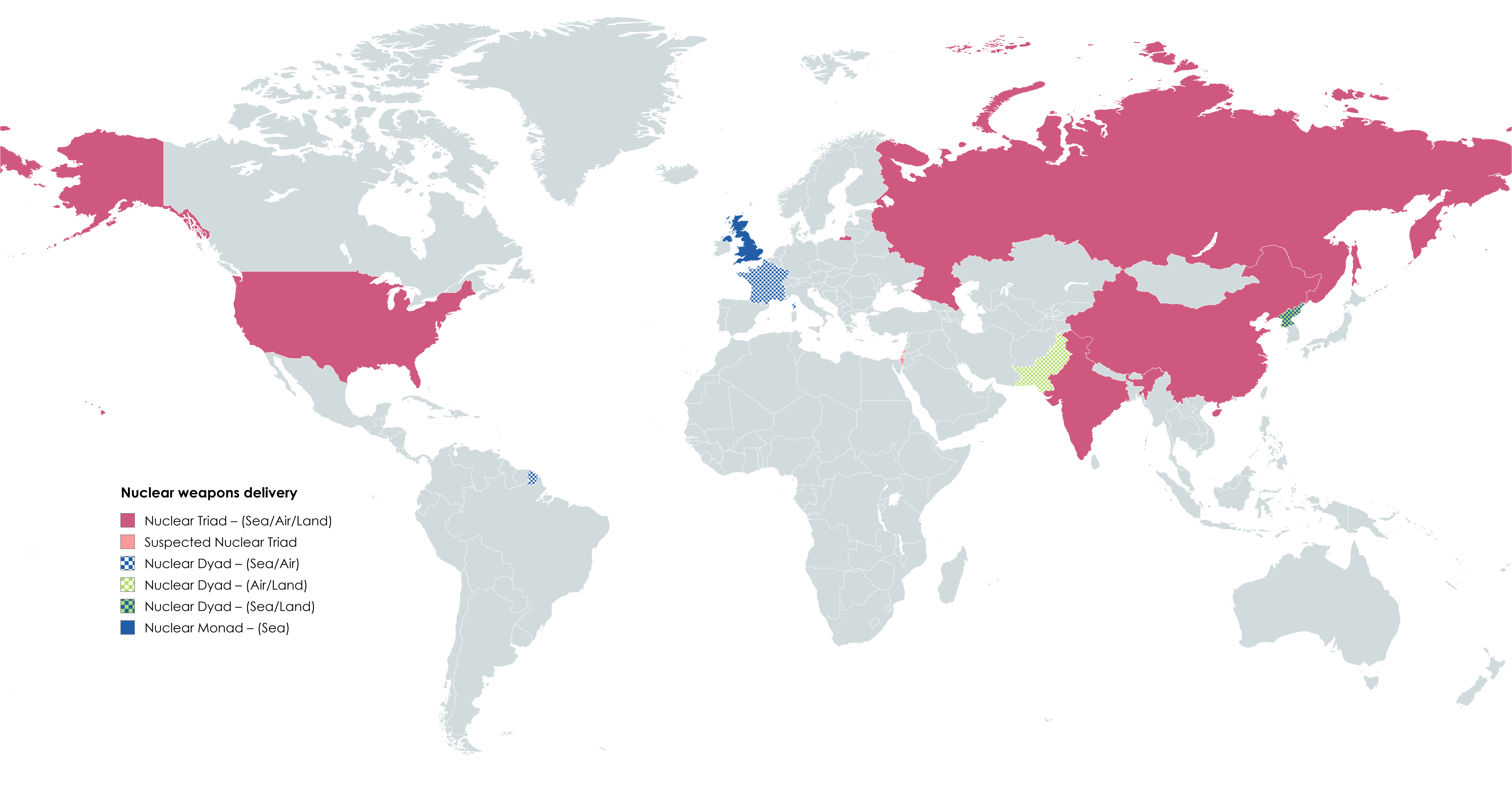
The "Nuclear Triad, Dyad, and Monad Nations Map" provides a comprehensive overview of the countries possessing nuclear capabilities, categorized into three distinct groups: triad, dyad, and monad nations. This visualization highlights the complex landscape of global nuclear power, illustrating which nations maintain various systems of nuclear deterrence and the implications of their arsenals. A nuclear triad refers to a country that possesses three delivery systems: land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers. In contrast, dyad nations have two of these systems, and monad countries possess only one. Understanding these classifications is crucial for comprehending international relations and military strategies in the contemporary world.
Deep Dive into Nuclear Capabilities
Nuclear weapons have shaped global politics since their inception, and the concept of a nuclear triad, dyad, or monad is central to the deterrence strategy employed by nuclear-armed states. The triad system, which includes ICBMs, SLBMs, and bombers, is considered the most robust form of nuclear deterrence. Countries like the United States and Russia exemplify this approach, maintaining a diverse arsenal that ensures a second-strike capability, thereby deterring potential aggressors. Interestingly, the redundancy provided by these three platforms allows for a more resilient defense strategy.
The U.S. maintains over 3,800 nuclear warheads, with a significant portion deployed on submarines, making them both stealthy and hard to target. Russia, with a similar number of warheads, relies on a mix of modernized systems and legacy platforms, ensuring their place as a dominant nuclear power.
On the other hand, dyad nations, such as China and France, rely on a combination of land-based missiles and submarine platforms, foregoing the strategic bomber option. China's nuclear strategy has significantly evolved, focusing on increasing its second-strike capabilities while maintaining a smaller overall arsenal compared to superpowers. France's nuclear deterrent, while smaller, is notable for its technological sophistication and integration with NATO operations.
Monad nations are relatively rare and usually possess a single delivery method. India, for instance, primarily relies on land-based ICBMs, while North Korea has focused on developing its missile technology to enhance its nuclear posture. Both countries face unique geopolitical challenges, as their capabilities influence regional security dynamics.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map by regions, it becomes apparent that nuclear capabilities are concentrated in specific areas, primarily North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. The United States and Russia dominate the triad category, while countries like the United Kingdom and France exemplify the dyad approach. Interestingly, South Asia has emerged as a critical flashpoint, with both India and Pakistan developing their nuclear arsenals amidst ongoing tensions.
In East Asia, China’s expansion of its nuclear capabilities is a focal point, especially in the context of its relationship with the United States and Taiwan. Meanwhile, North Korea's aggressive stance has led to increased military posturing in the region, forcing neighboring countries to reassess their security strategies. The differences in nuclear policy and strategy reflect the unique historical and political contexts of each nation, making regional comparisons essential for understanding global security dynamics.
Significance and Impact
The implications of nuclear triad, dyad, and monad classifications extend far beyond mere military strategy; they shape diplomatic relations, influence arms control negotiations, and affect international security architectures. The ongoing debates surrounding nuclear disarmament highlight the tension between nations seeking to maintain their deterrent capabilities while addressing global calls for non-proliferation.
As we witness technological advancements in missile defense systems, cybersecurity, and hypersonic weapons, the landscape of nuclear deterrence is evolving. Countries are increasingly challenged to adapt their strategies to address new threats while maintaining their deterrent credibility. The future of nuclear policy will likely hinge on the delicate balance between ensuring national security and fostering international stability.
Ever wondered why some nations are more vocal about their nuclear capabilities than others? The answer often lies in how these nations perceive their security environment and the threats they face. Understanding the nuances of nuclear capabilities offers valuable insights into international relations today and highlights the critical importance of diplomacy in mitigating nuclear risks around the world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 9, 2025
- Views
- 130
Comments
Loading comments...