High Speed Railways Daily Frequency Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
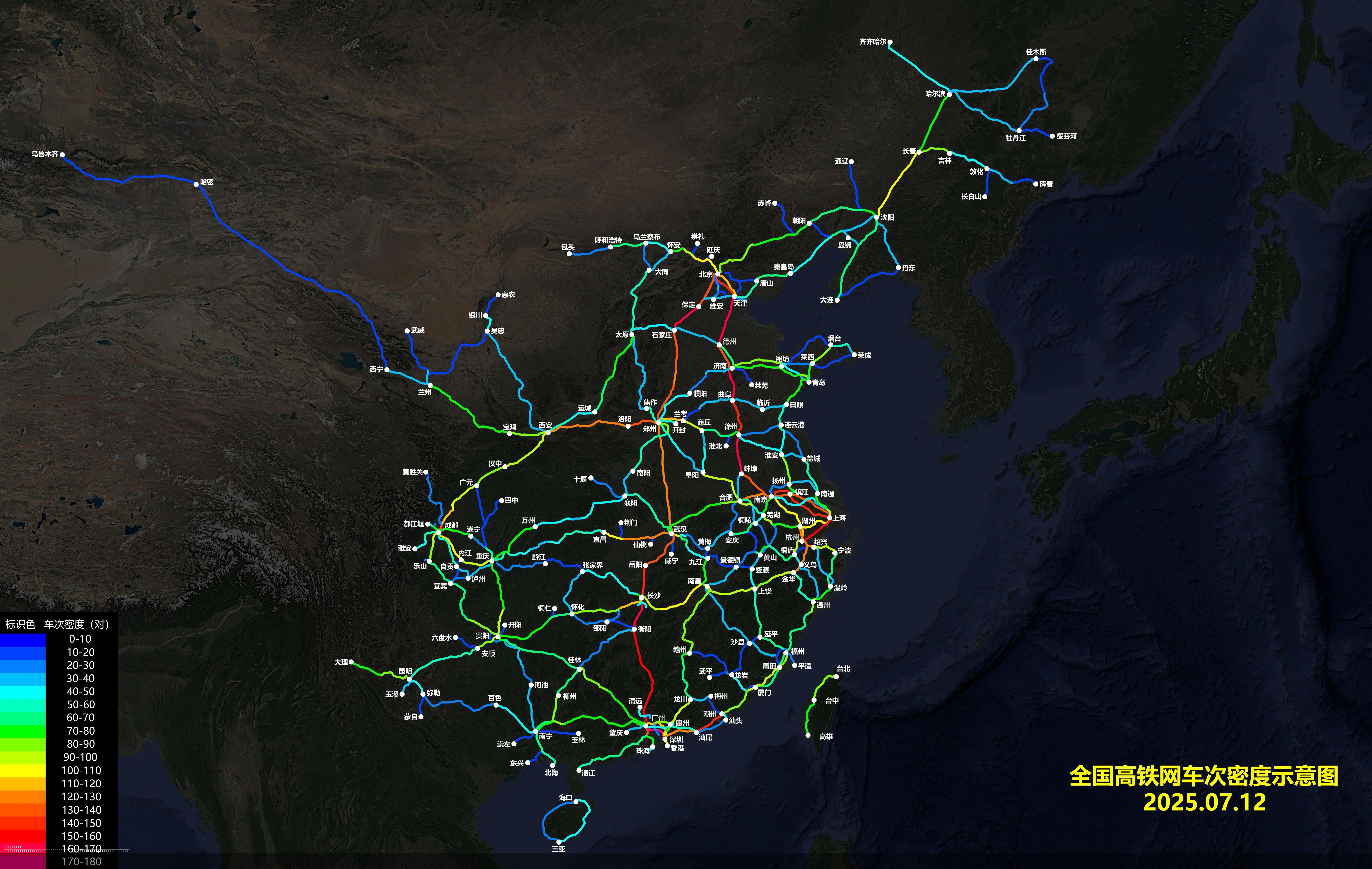
What This Map Shows
The "Daily Frequency Map of High Speed Railways in China and Taiwan" offers a visually striking representation of high-speed railway networks across these two regions as of July 12, 2025. This visualization highlights the intricate web of rail lines, showcasing the frequency of trains operating on these routes each day. By observing this map, viewers can quickly grasp which areas are served by frequent high-speed trains and how these connections facilitate travel between major cities.
Deep Dive into High-Speed Railways
High-speed rail (HSR) has transformed transportation in many countries, and none more so than in China and Taiwan. China boasts the most extensive high-speed rail system in the world, with over 40,000 kilometers of track. The average speed of these trains often exceeds 300 kilometers per hour, allowing passengers to traverse vast distances in remarkably short timeframes. The introduction of HSR has not only reduced travel times but has also encouraged economic growth and regional development.
Interestingly, China’s high-speed rail network began its rapid expansion in the early 2000s. This ambitious project aimed to connect major urban centers to improve accessibility and reduce the burden on traditional rail and road transport. By 2025, the map illustrates that cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen are interconnected with frequent daily services, which has greatly enhanced commuter convenience and business connectivity. For instance, a trip from Beijing to Shanghai, which used to take nearly 13 hours, now takes less than 5 hours.
In Taiwan, the high-speed railway system, operational since 2007, has also made significant strides. The Taiwan High Speed Rail (THSR) covers approximately 345 kilometers along the western corridor, linking Taipei and Kaohsiung with a travel time of around 90 minutes. Despite its smaller scale compared to mainland China, THSR has dramatically impacted daily life, allowing for efficient travel between major urban centers and contributing to economic integration on the island.
What’s fascinating is how these rail networks have led to a shift in population dynamics, as people can now live farther from their workplaces and still commute easily. The accessibility provided by high-speed rail has made it viable for individuals to work in urban centers while residing in suburban or even rural areas. This phenomenon also raises questions about urban planning and infrastructure development.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map, it's clear that the frequency of high-speed trains varies significantly between regions in both China and Taiwan. In China, the eastern coastal cities receive the highest frequency of services. For instance, the Beijing-Shanghai corridor is one of the busiest, with trains running every few minutes during peak times. Conversely, more remote areas, such as those in the northwest, have limited frequency, reflecting the uneven economic development across the country.
In Taiwan, the high-speed rail serves a more compact area, and thus the frequency across its stations is relatively uniform, but it still demonstrates regional disparities. The western corridor, being the most populous and economically dynamic, sees trains operating at high frequency compared to the eastern regions, which are less developed and have fewer passengers. The map highlights these differences, with frequent services represented by darker colors and sparser routes indicated by lighter hues.
Significance and Impact
The implications of high-speed railways extend beyond mere transportation. They are pivotal in shaping the economic landscape, influencing urban development, and even impacting environmental sustainability. As regions become more interconnected, there is a notable increase in trade, tourism, and cultural exchange. High-speed rail systems are also seen as a greener alternative to air travel and long-distance road transport, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Current trends indicate that as nations continue to invest in high-speed rail, we can expect further expansions and enhancements to existing networks. In China, the government plans to increase the total length of high-speed rail lines significantly by 2030, aiming to reach over 70,000 kilometers. Meanwhile, Taiwan is exploring potential extensions of its rail network to reach more remote areas and enhance connectivity.
In conclusion, the high-speed railways of China and Taiwan not only reflect advances in transportation technology but also play a crucial role in shaping the socio-economic fabric of these regions. As we look towards the future, the continued development of these networks will undoubtedly influence patterns of living, working, and connecting in an increasingly mobile world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 5, 2025
- Views
- 134
Comments
Loading comments...