
Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
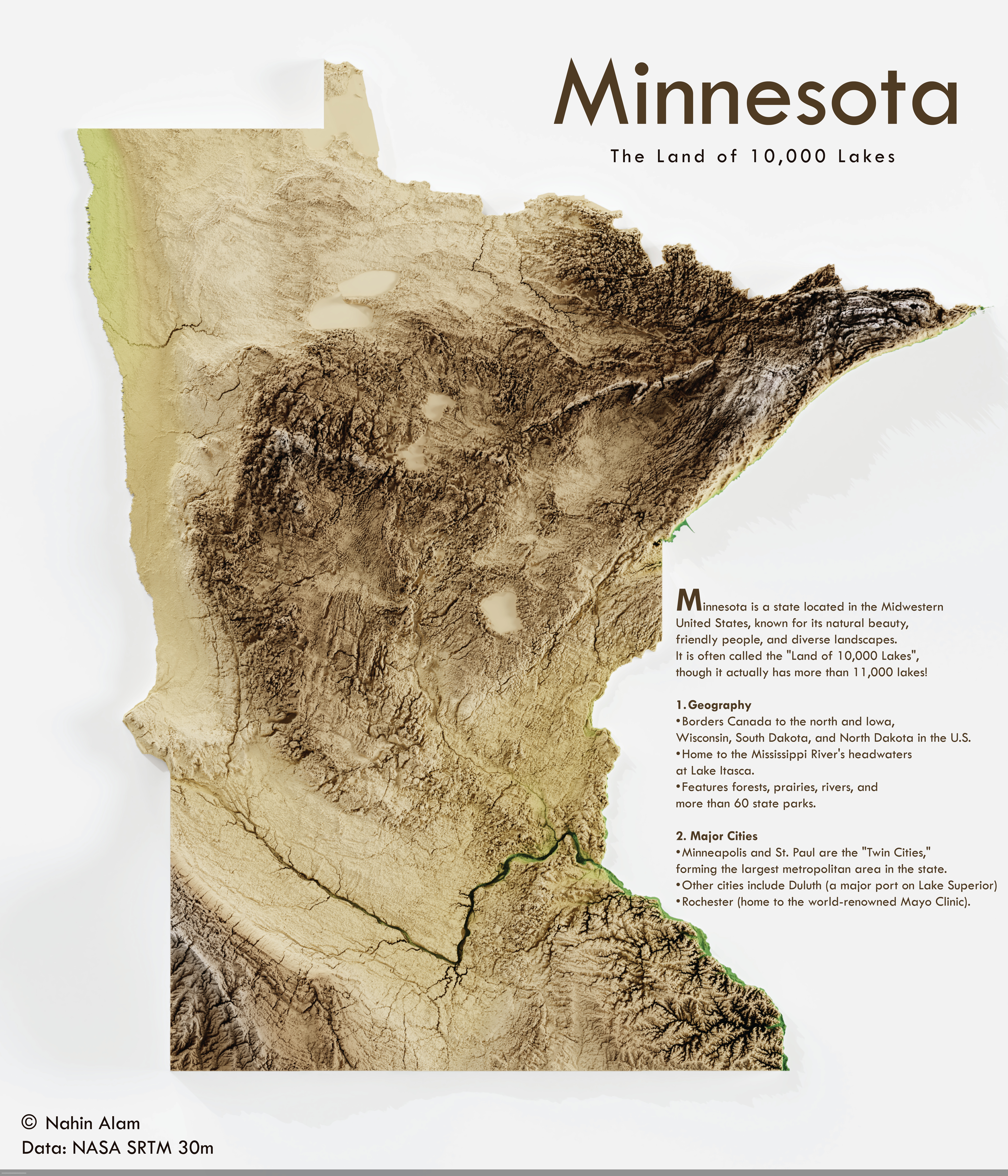
The Shaded Relief Map of Minnesota provides a three-dimensional perspective of the state's diverse topography. By using shading techniques, the map highlights the elevations and depressions across the landscape, making it easier to visualize the state's rolling hills, lakes, rivers, and valleys. This type of map is particularly useful for understanding Minnesota's geographical features, which are crucial for both natural processes and human activities.
Deep Dive into Minnesota's Topography
Minnesota is often referred to as the Land of 10,000 Lakes, and this title is not just a catchy phrase; it reflects the state's abundant freshwater resources. The lakes, along with the rivers and streams, are a result of glacial activity that sculpted the landscape during the last Ice Age. The state’s terrain is primarily characterized by three major regions: the northern forested areas, the central agricultural plains, and the southern urbanized zones.
Interestingly, the northern part of Minnesota is dominated by the Laurentian Highlands, which rise above 1,000 feet in elevation. This region includes the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness, known for its pristine lakes and rugged terrain. The shaded relief map illustrates how these highlands create a dramatic contrast with the flatter plains to the south. The elevation changes are not just visually striking; they also impact the climate and ecosystems found in different parts of the state.
In contrast, the central region of Minnesota is largely agricultural, with fertile soil that supports a variety of crops. The elevation here is much lower, averaging around 1,000 feet, which facilitates farming. The shaded relief highlights the gentle slopes and valleys that are typical of this area, providing a clear visual representation of how geography influences land use.
The southern part of Minnesota, particularly around the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul, showcases an urbanized landscape. The elevation here is generally lower, which aligns with the Mississippi River flowing through the area. The shaded relief map reveals how the river has carved its way through the landscape, creating bluffs and valleys that are critical for both city planning and recreation.
Regional Analysis
Examining Minnesota through the lens of the shaded relief map allows for a deeper understanding of the state's diverse regions. For example, the northwestern region, which includes the Red River Valley, is primarily flat and has a different agricultural profile compared to the hilly terrain of southeastern Minnesota, which is known for its vineyards and apple orchards.
In the northeastern part, the Arrowhead region is characterized by rugged terrain, with notable peaks like Eagle Mountain, the highest point in Minnesota at 2,301 feet. The shaded relief map effectively showcases these geographical distinctions, revealing how elevation impacts everything from climate to biodiversity.
Have you noticed how the variations in elevation can lead to different vegetation types across the state? The northern forests are predominantly coniferous, while the southern regions feature deciduous trees. This transition is gradual but significant, reflecting how geography shapes ecological zones.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Minnesota’s topography through the shaded relief map is essential for numerous reasons. Firstly, it helps in environmental conservation efforts, as different elevations can host unique ecosystems that require specific protective measures. Secondly, this knowledge is vital for urban planning and infrastructure development. For instance, areas prone to flooding can be identified more easily by examining the landscape’s elevation, which is crucial for sustainable development.
With climate change increasingly affecting weather patterns, understanding how topographical features influence local climates becomes even more critical. For example, higher elevations may experience more snowfall in winter, leading to implications for water supply and local ecosystems during the spring thaw.
Interestingly, as urbanization continues to expand in Minnesota, particularly around the Twin Cities, the balance between conserving natural landscapes and accommodating growth becomes a pressing issue. The shaded relief map serves as a reminder of the natural beauty and complexity of Minnesota’s geography, urging us to consider how we can live harmoniously with our environment.
In conclusion, the Shaded Relief Map of Minnesota is not just a tool for navigation or geography; it’s a gateway to understanding the intricate relationships between landforms, ecosystems, and human activities. By appreciating the state’s topography, we can make more informed decisions about conservation, development, and resource management in the future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 3, 2025
- Views
- 116
Comments
Loading comments...